Stages of the process of making managerial decisions on an example. Examples of management decisions in the organization. Examples of programmed management decisions in an organization
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Similar Documents
Basic concepts, classification groups and types management decisions. The essence of decisions and the order of their development. Evaluation of the effectiveness of managerial decision-making and methods of their analysis. Making a decision on the example of the company LLC "Your sausages".
term paper, added 06/19/2011
Concept, essence and characteristics management decisions. The main stages of development of management decisions. Factors influencing decision making. Practical use typology of managerial decisions on the example of the organization OOO "Medenta".
term paper, added 01/06/2015
Information support of the process of making managerial decisions. Implementation of decisions in the organization. Analysis and adoption of managerial decisions in conditions of certainty and uncertainty. Implementation of management decisions at the company OOO "Tsimus".
term paper, added 05/13/2010
Defining the goals and value system of the enterprise. Necessity, technique and methods of decision-making. Stages of development of management decisions. Development of a management decision by the method of collective generation of ideas. Basic principles of forecasting
term paper, added 02/22/2009
The essence and procedure of the decision-making process. Brief classification of management decisions. Inventory management models. Analysis and management decision-making under risk, conflict and uncertainty. Bounded rationality model.
term paper, added 10/03/2013
Features and classification of management decisions. Factors influencing management decision making. The main stages of the process of developing and making a management decision. Factor classification internal environment for specialized functions.
term paper, added 05/25/2014
The role of management decisions in the process of management, planning, organization, coordination and control. Decision making under uncertainty, the need to apply modeling in manufacturing organizations. Analysis of the decision-making process.
test, added 05/19/2010
Introduction
The relevance of the topic is determined by the fact that the life process of each organization is associated with the process of continuous change and development. An organization can achieve its goals only if its changes are adequate to the changes and requirements of the existing economic environment of market relations.
For state of the art science is characterized by a transition to a global consideration of the degree of development of the problem "Technology for making managerial decisions", many works are devoted to research issues. Basically, the material presented in the educational literature is of a general nature, and in numerous monographs on this topic, narrower issues of the problem "Technology for making managerial decisions" are considered. However, accounting is required modern conditions in the study of the problems of the designated topic.
The high significance and insufficient practical development of the problem "Technology for the adoption of SD on the example of a commercial enterprise" determine the undoubted novelty of this study. Further attention to the issue of "Technology for the adoption of SD" is necessary in order to use modern technologies decision-making is important for the leader, one of the main professional skills which is the ability to make effective management decisions. And in the fierce competition with other equal conditions successful, sustainable development and survival of those organizations that put themselves at the service of additional opportunities provided by technologies for making managerial decisions.
The topic of this work is the technology of making managerial decisions on the example of a trading enterprise CJSC "Vneshtorgsib - M"
The object of the study is the activity of wholesale - retail enterprise CJSC "Vneshtorgsib - M".
The subject of the research is the development of management decisions at the enterprise.
The purpose of the thesis is to study and evaluate experience, develop effective technologies in the process of preparing, making and implementing management decisions, as well as developing recommendations for their improvement.
To achieve this goal, it is necessary to solve the following tasks:
1. To reveal the theoretical foundations for the development of management decisions.
2. Identify problems in the development of management decisions.
3. Investigate the development of management decisions at CJSC Vneshtorgsib-M.
4. Suggest ways to improve the development of management decisions at CJSC Vneshtorgsib-M.
The following research methods are used in the thesis work: theoretical analysis of documentary and literary sources, analysis of documents, interview. The received research material was significantly supplemented by such a method as participant observation.
Knowledge. A significant contribution to the study of the problems of management efficiency, organization behavior in solving the set goals was made by economists and practitioners I. Ansoff, H. Wissema, P. Drucker, M. Porter, G. Simon, A. Strickland, S. Fisher and others. V.V. Glushchenko, A.G. Ivasenko, I.D. Ladanov, A.E. Saak, L.E. Sokolova and others. E.I. Brazhko, E.P. Golubkov, O.S. Vikhansky, I.L. Kardanskaya, L.I. Lukicheva, R.A. Fatkhudinov, E.Yu. Khrustalev, L.P. Yanovsky and others.
Of the foreign authors who worked on the problem under study: T. Boydell, N. Winner, F. Kotler, R.D. Lewis, M.H. Mescon, M. Albert, F. Hedouri, F. Harrison and others. Practical significance. The methodology and results of the study can be useful for organizing types of service industries. The developed recommendations make it possible to improve and improve the management decision-making system at the ZAO Vneshtorgsib-M enterprise.
The sources of information for writing a paper on the topic "Technology for making a managerial decision" were the basic accounting and reporting information on the enterprise CJSC "Vneshtorgsib - M" for 2004 - 2007.
The practical significance of the work lies in the fact that the developed recommendations make it possible to improve and improve the management decision-making system at the enterprise CJSC Vneshtorgsib-M.
Work structure. The study consists of an introduction, three chapters, a conclusion and a bibliographic list. The introduction substantiates the relevance of the choice of topic, sets the goal and objectives of the study, characterizes the research methods and sources of information.
Chapter one reveals general questions, reveals the historical aspects of the problem "Technology for making managerial decisions". The basic concepts are determined, the relevance of the sounding of the questions "Technology for making a managerial decision" is determined.
In chapter two, the content and modern problems of "Technology for making managerial decisions" are considered in more detail.
Chapter three is of a practical nature and, on the basis of individual data, an analysis of the current state is made, as well as an analysis of the prospects and trends in the development of "Technology for making managerial decisions".
Chapter 1. Theoretical basis development of management decisions
1.1 Essence and characteristic features of management decisions
There are many definitions and interpretations of the concept of "management decision". Here are some of them:
1. A management decision is the result of analysis, forecasting, optimization, economic justification and choosing an alternative from a variety of options to achieve a specific goal of the management system.
2. Management decisions are, first of all, the creative and volitional influence of the subject of management, based on knowledge of the objective laws of the functioning of the managed system and the analysis of management information about its state, aimed at achieving the goal.
3. A managerial decision is a choice that a leader must make in order to fulfill the responsibilities due to his position. The global goal of developing and adopting any management decision is to provide a feasible and most effective option for moving towards the goals set for the organization.
4. Management decision is a creative act of the subject of management, aimed at eliminating the problems that have arisen in the management object.
5. Management decision is a creative, mental act of the subject of management, which, based on the requirements, goals and emerging tasks and using data analysis and information about the object, determines the program for the subsequent activities of the team and individual workers.
6. A managerial decision is one of the necessary moments of volitional action, consisting in choosing the goal of the action and the methods for its implementation.
7. A managerial decision is the result of a specific managerial activity. Decision making is the basis of management. Each managerial function is associated with several general, vital decisions that need to be implemented.
8. Management decision is the result of analysis, forecasting, optimization, economic justification and selection of alternatives from a variety of options to achieve a specific goal of the management system.
9. A managerial decision is a deliberate conclusion, to take some action or, conversely, to refrain from them.
One of the basic concepts and components of the actions of entrepreneurship and management is the concept of "solution".
The decision is called the choice of alternatives of a certain course of action to achieve the goal.
An alternative is one option to achieve a goal that excludes another option.
Management decision is the basis of the management process. To manage means to decide. The term "management decision" is used in two main meanings - as a process and as a phenomenon:
Management decision as a process is the search, grouping and analysis of the required information; development, approval and implementation of management decisions;
· A management decision as a phenomenon is a plan of action, a resolution, an oral or written order, etc.
The essence of management decisions is associated with the social, economic, organizational, legal and technological interests of the organization (Figure 1.1).
Rice. 1.1 The essence of management decisions
The economic essence of management decisions is manifested in the fact that the development and implementation of any decision requires financial, material and other resources. Therefore, every management decision has its own cost. The implementation of an effective management decision should bring direct or indirect income to the company, and wrong decision leads to losses, and sometimes to the termination of the company.
The organizational essence of a management decision is that in order to develop and implement SD, a company must have the following capabilities, including:
Form a workable team;
Develop instructions and regulations governing the powers, rights, duties and responsibilities of employees;
Allocate the necessary resources, including financial and information;
Provide employees with the necessary equipment;
Establish a control system;
Constantly coordinate the process of development and implementation of SD.
The social essence of a managerial decision lies in the personnel management mechanism, which includes leverage on an employee in order to encourage him to vigorous activity a team. These levers include:
Needs; - interests;
motives of behavior; - installations;
Human values.
The legal essence of a management decision is the strict observance of regulatory legal acts, as well as the charter and other documents of the company itself. Violation of the law in the development of SD can lead to the cancellation of the decision, legal liability for its implementation.
The technological essence of a management decision is manifested in the possibility of providing personnel with the necessary technical, information tools and resources for the development and implementation of SD. When planning the development and implementation of SD, the manager must simultaneously form a technological basis for it.
Through the solution, the goal, types, scope of activities, rights and responsibilities are established, the actual state of phenomena, objects at a given time, etc. is fixed.
Accordingly, a management decision is reflected in the form of various kinds of documents, for each form of development of a management decision, its own set of implementation forms is used (Fig. 1.2).

Rice. 1.2 Joint use of forms for the development and implementation of management decisions
Describing the reasons for the need for decision-making, it seems possible to single out decisions:
1. logically determined by the technology of the process;
2. random, the need for which arises if the problem is generated by factors that may or may not appear when goals are achieved.
Management decisions are usually classified according to the following grounds (Fig. 1.3, 1.4).
1. Depending on the degree, managerial decisions causing the need for development and adoption are divided into programmed, non-programmed.
Highly structured, i.e. resulting from the implementation of a certain sequence of actions and steps;
Weakly structured (non-programmed), required in situations that are new to a certain extent, not internally structured or associated with unknown factors.
2. By reason (nature of acceptance):
Intuitive decisions - a choice made only on the basis of a feeling that it is correct;
Based on judgments, accepted on the basis of knowledge and experience. They are based on a forecast of future results. The method guarantees the prevention of gross errors.
The rational way of solving problems is called the best. It involves the formulation of all possible alternatives, the development of a system of the preferred option.
3. According to the degree of novelty:
Traditional decisions make up about 90% of decisions made in recurring situations. They are mainly used at the middle and lower levels of management.
Decisions made in new situations, to solve new problems, are called original. They require collection and analysis additional information and manifestation of innovative abilities of the leader.
4. According to the degree of certainty:
5. By nature:
Strategic decisions - decisions regarding a set of actions aimed at achieving the goals of the organization through its adaptation (adaptation) to changes in the external environment.
Current solutions - solutions that develop and refine promising solutions and accepted within a subsystem or phase of one of its cycles, such as the development cycle.
Operational decisions - decisions covering production processes for the manufacture and supply of elements of a lower level, bringing the planned task to specific performers in each division.
6. By functional orientation:
Planning - based on a special study to form a conclusion about the possible development and results of any management process;
Organizational - provide for the formation of a new or improvement of the existing structure of the company's management, as well as a set of administrative measures to organize the implementation of the task;
Activating - to increase the efficiency of the task, they form decisions to enhance the activities of the company's employees through stimulation and mobilization;
Coordinating - in the event of the appearance of unforeseen interfering influences, they are necessary to harmonize the company's activities;
Controlling decisions are aimed at ensuring the timely implementation of plans and planned development milestones;
Informing decisions are aimed at familiarizing the initiators and executors of the decision with the information they need, as well as with the intermediate and final results of the task.
7. For reasons:
Situational management decisions are caused by events that disrupt the planned course of events. Usually these are current, daily decisions of the head. A large number of them indicates an inefficient management process and the possibility of a crisis.
Management decisions on prescription are determined by the relevant regulations.
Program management decisions are long-term and universal in nature, determine the main directions of development, are the basis for more detailed decisions designed to ensure the achievement of program objectives at each stage of its implementation within a certain timeframe.
Initiative decisions are made by managers who occupy a fairly high, dominant position.
8. According to the degree of regulation:
Regulatory decisions must be implemented, and do not imply any initiative.
Orienting decisions determine the possible options for the activities of employees, when certain conditions occur.
9. According to the number of criteria:
Single-criteria decisions allow evaluating alternatives based on one criterion (indicator), the degree of importance of which may depend on objective conditions or be determined subjectively by the decision maker.
When evaluating multi-criteria decisions, a system of indicators is used. This creates the necessary difficulties, since it is necessary to select and evaluate their impact on the final result.
10. By organization:
The individual form of organization of managerial decision-making is characterized by the fact that the head alone (individually) makes a decision and bears personal responsibility for it.
At collective form all team members participate in the decision-making process (based on voting or consensus).
The collegial form of decision-making means that the work of preparing and making a decision is performed by a group of specialists authorized for this by a team of employees.
Decisions that have quantitative characteristics (approval of the budget, attraction of investments, setting tariffs for land lease services).
Decisions that do not have quantitative characteristics (the formation of a corporate culture, the solution of personnel issues, the management of public relations) are subjective, since they are determined by the personality of the subject who makes them.
12. Direction:
Decisions for influencing the external environment of the enterprise concern the immediate environment, partners, customers, creditors;
Decisions for influencing the internal environment of the enterprise are associated with a managed system (for example, a change in the staffing table, which will entail a reduction in employees or the development of a new management structure, as a result, a new position of a top manager will appear).
13. By scale:
General - affect the entire enterprise, its production and financial and economic activities. General management decisions determine fundamental changes in the enterprise, as well as the further development of production (computerization of production and management processes, the transition to production new products, reorganization of the enterprise, etc.);
Private - relate to any subsystems that affect current issues (for example, about discipline, about dismissal of an employee, about changing the work schedule of a department, etc.).
14. According to the degree of alternativeness:
Certainty - the choice of an alternative in conditions where the results of each of the options are known exactly;
Uncertainty - the choice of an alternative in the face of the impossibility of assessing the likelihood of potential outcomes;
Probabilistic certainty - the choice of an alternative in the face of ambiguity in the results of the options.
15. By the nature of development and implementation (by style):
Balanced decisions imply that the efforts of the decision maker to find and evaluate alternatives are distributed approximately equally. These solutions are effective for performers with high classification and high self-esteem;
Impulsive decision implies that the preparation of alternatives takes much longer than the assessment, and the decision is subjective and risky. For the effective implementation of impulsive decisions, a high personal and professional authority of the leader among subordinates and his high charisma are required;
Inert decisions mean that the process of finding different solutions is slow and uncertain. Such decisions are secondary, and the cost of justifying them far exceeds the effort spent on finding options. They weakly activate the staff to implement decisions. Inert solutions are effective in the current process of management activities, good support from managers at all levels, and also, if possible, to lobby their interests in the external environment.
Risky decisions are characterized by a higher intensity of work at the stage of searching for alternative options than at the stage of their evaluation. Such decisions are characteristic of gamblers - players. These solutions are effective in the general positive attitude of the leader and performers, when a possible failure does not significantly worsen the material and social condition of the team. Risky decisions usually use insurance or other methods to reduce possible damage; Cautious decisions are characterized by the thoroughness of the leader's collection of all options, a critical assessment of alternatives, and a large number of approvals. Such decisions are effective in resolving problems related to human life and the state of its environment. For example, decisions related to the activities of personnel at nuclear, thermal and power plants
The composition, structure, content and form of management decisions are determined by the specified criteria and the classification basis. So, for all their potential value, decisions will remain only good wishes if they are not translated into concrete actions. It is better not to start a business at all than to make unfavorable, and even unlawful decisions only on the grounds that they are well known, convenient, or suit someone.
The main means of managerial activity that determine the technology of its implementation are information support, organizational management techniques, conditions for managerial activity (organization of the workplace) and, of course, professional, business, socio-psychological and other personal qualities of the subject of activity.
1.2 Main elements of management decisions, basic requirements for them
The result of the manager's work is a managerial decision. The whole activity of the organization depends on what this decision will be, it also depends on whether the goal will be achieved or not. Therefore, the adoption of a decision by a manager always presents certain difficulties. This is due both to the responsibility that the manager takes on and to the uncertainty that is present when choosing one of the alternatives.
The main element of each managerial decision-making process is the problem, which is understood as the discrepancy between the actual state of the managed object (for example, in the provision of services) to the desired or given, i.e., the goal or result of the activity. The development of a plan of action to eliminate the problem is the essence of the decision-making process.
The simplest, "ideal" decision scheme in Figure 1.5 assumes that the process is a co-current movement from one stage to the next; after identifying the problem and establishing the conditions and factors that led to its occurrence, solutions are developed, from which the best is selected.

Rice. 1.5 Steps in the decision-making process
A more detailed structuring of the decision-making process is shown in Figure 1.6, where each of the stages (statement of the decision-making problem, decision-making, choice and implementation of the decision) highlights the procedures necessary to implement the targets of each stage.
Thus, the basis for setting the decision-making problem is the occurrence of a situation that causes the appearance of a problem. The description of the problem situation gives an idea of the factors that need to be carefully analyzed and considered when solving. First of all, it is required to establish whether they are internal or external in relation to this organization, since the possibilities of influencing these two groups of factors are different.
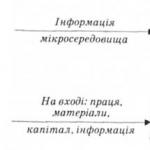
To internal environmental factors wholesale - retail companies, to the greatest extent, include: development goals and strategy, production and management structure, financial and labor resources, procurement and sourcing, marketing, inventory management. They form an enterprise as a system, the interconnection and interaction of elements of which ensures the achievement of its goals. Therefore, a change in one or more factors at the same time causes the need to take measures of managerial influence aimed at preserving the properties of the system as an integral entity.
The first group of external factors is practically uncontrollable by the managers of the organization, but it has an indirect (indirect) influence on its activities, which must be taken into account. It refers to the state of the macroeconomic environment in which a particular industry operates. Usually these are economic socio-demographic, political, legal and technological factors. For example, the economic state of a country (region) affects the work of an organization through such environmental parameters as the availability of capital and labor, price levels and inflation, labor productivity, buyers' income, government financial and tax policies, etc. Thus, inflation leads to a reduction in purchasing power. ability and reduces the demand for the products produced by the organization. An increase in the level of prices for products of related industries causes a corresponding increase in production costs in the organization, which results in an increase in prices for its products and can cause an "outflow" of a certain group of consumers. When their incomes are reduced, buyers change the composition and structure of consumption, which can also affect demand. The level of scientific and technological development in the country has a strong influence on the structure of the economy, on the processes of automation of production and management, on the technology by which products are manufactured, on the composition and structure of the personnel of organizations, and, most importantly, on the competitiveness of products and technologies. Accounting for numerous and diverse environmental factors, choosing the main ones among them and foreseeing possible changes in their mutual influence is the most difficult task facing leaders and managers.
The second group of external factors are less susceptible to influence by the managers of the organization. It includes the state of the microeconomic environment, which denotes aspects of the external environment that directly affect the organization due to its close interaction with the internal structures of the organization. In such a business environment, competitors, suppliers, consumers, labor markets and financial institutions operate, which initially shape the plans and activities of the company.
A necessary element (and parameter) of the managerial decision-making process is the assessment of the actions that are taken at its various stages.
A managerial decision is a decision made in trading system and directed: management of managed activities; marketing planning; financial planning; control by human resourses; interaction with the internal and external environment.
Thus, the decision-making process in retail trade should be carried out taking into account the characteristics of this area of the economy, as well as the influence of internal and external factors and constraints. This will help improve the quality and validity of decisions at all levels of management.
At the first stage, the target setting is most often used as a criterion for recognizing a problem, by the deviation from which the problem is judged.
The decision development stage begins with the collection and processing of the information necessary to develop a course of action.
At the stage of selecting and implementing a solution to a problem, various criteria are applied to select from a variety of project proposals acceptable ones, and from them - the most useful or preferable for solving the organization's goals. The quality of management decisions depends on how reasonably they are chosen, and this, in turn, determines the competitiveness of the organization, the speed of its adaptation to changes in the economic situation and, ultimately, efficiency and profitability.
Decision makers are called decision subjects. These may be individuals or groups of managers who have the authority to make decisions. In addition, experts can be involved in the process of development and decision-making at all its stages - specialists in specific problems, procedures, stages. Experts can provide significant assistance in setting the problem, in developing possible situations; they can set goals and set limits, develop solutions and evaluate their consequences, and so on. Experts are responsible for their recommendations.
Management decisions developed and adopted in organizations affect the interests of many people. The leader must be able to explain to the performers, top management, why he made this or that decision. There are a number of requirements for a managerial decision table 1.1.
Requirements for management decisions and conditions for achieving
| Requirements for SD and conditions for their preparation and implementation | Conditions for achieving requirements |
| 1. Compliance of SD with the current legislation and the company's statutory documents | 1.Self-control 2.control by a lawyer, referent |
| 2. Availability of official powers (rights and responsibilities) for the RDP | 1. Implementation of job descriptions 2. Availability of complete and reliable information about departments and services |
| 3. The presence in the text of SD of a clear target orientation and targeting (executors should be clear what the solution being developed is aimed at and what means will be used) | 1. Bringing to each performer his role in management decisions 2.Formulirovka for each purpose, timing, resources. |
| 4. Correspondence of the SD form with its content | Control by a lawyer, referent |
| 5. Achieving timeliness (no rush or late) | 1. Knowledge and intuition of the leader 2. Real assessment of the situation |
| 6. The absence in the text of the solution of contradictions to itself or previously implemented solutions | 1.Self-control 2. Control by a lawyer, referent |
| 7. Possibility of technical, economic and organizational feasibility of SD | 1. Conclusion of specialists who understand the problem 2. Conclusion of the company's experts |
| 8. Availability of parameters for external or internal control of SD implementation | 1. Operational control 2.Professional audit |
| 9. Accounting for possible negative consequences in the implementation of SD in the economic, social, environmental and other areas | 1.Conclusion of external experts, 2.Risk assessment |
10. Possibility of a reasonable positive result |
1. set (complex) of calculations for risky events 2. assessment of the true value of this management decision 3.Strategic forecasts for the development of the company in the implementation of this decision |
So, the presented scheme of the decision-making process reflects the logic of management activity, and not its complexity. In practice, this process is more complex and allows not only the sequence, but also the parallelism of a number of procedures, which can significantly reduce the decision-making time. It helps to identify important problems of a particular company, as well as the degree of uncertainty in which it operates. The effectiveness of this process largely depends on the methods that managers and leaders operate in performing all the necessary types of managerial work.
1.3 Algorithm and methods for making managerial decisions
The most important organizational aspect of the development and implementation of management decisions is the organization of the sequence of work required to complete this process. Here, the type of management that exists in the enterprise is of particular importance.
The theory of algorithms defines the concept of "algorithm" as a precise prescription that determines the process of information transformation. Decision development algorithm - a logical sequence of operations for the development of a management decision
Consider possible algorithms for the development and decision-making process for various types of management.
1. Under traditional management:
Identification of the problem;
Collection of information;
Information analysis;
Identification of the problem from the previous one;
Forecasting by analogy;
Evaluation and verification of solutions;
Adoption, registration, bringing to the executors of the decision, its execution, control of implementation.
Thus, decision-making in traditional management is based on studying past experience in solving similar problems, as well as predicting consequences by analogy with previously observed consequences. These features leave their mark on the decision-making algorithm, which includes stages related to the identification of a similar problem and the prediction of results by analogy with those already obtained.
2. With system management:
Identification of the problem;
Collection of information;
Analysis of information about the system as a whole and about the relationships of its elements;
Problem diagnosis;
Determining the goals of element management when solving a problem at the system level;
Development of criteria for evaluating the effectiveness of the solution;
Development of options for possible actions on the subsystem that is the source of the problem;
Predicting these actions for the system as a whole;
Evaluation and verification of these actions;
Acceptance, registration, bringing to the performers, execution, control of execution.
Thus, in system management, when understanding the organization as a set of interrelated elements, decision making is based on the analysis of information about the system and its components, as well as predicting the consequences for the elements of the system and the system as a whole.
3. With situational management:
Identification of the problem;
Gathering information about the situation;
Analysis of information about the situation;
Diagnosis of the problem and situation;
Determining the goals of managing the situation in solving the problem;
A list of possible actions to resolve the situation, forecasts of their consequences;
Verification, evaluation of solutions;
Adoption, execution, bringing to the executors, execution, control over the implementation of decisions.
The situational approach focuses on the fact that the suitability of various management methods is determined by the situation, therefore, the decision-making algorithm includes the stages of collecting and analyzing information about the situation, determining the goals of managing the situation when solving a problem, and predicting the consequences of control actions for the situation.
4. With social - ethical management:
Collection and analysis of information about the managed object (about problems and how it was solved);
Problem definition;
Determining the goals of solving the problem;
Development of criteria for evaluating an effective solution;
Prediction of consequences for various solutions;
Development of criteria for the optimal solution;
Verification of options;
Choosing the optimal solution;
Design, bringing to the performers, execution, control.
In social and ethical management, special attention in decision-making is paid to taking into account the permissible and not permissible consequences of options for control actions for various parameters.
5. With stabilization management:
Identification of the problem;
Collection of information about changing parameters;
Information analysis;
Problem diagnosis;
Determination of management objectives when solving a problem;
Development of decision evaluation criteria;
Study of the dynamics of the parameters of the control object;
Determining the time during which the object can still be stably controlled;
Distribution of available time for the preparation and execution of decisions to stabilize the managed object;
Development of solutions;
Forecast of the consequences of their application;
Evaluation of the implementation of various options;
Choosing the best option;
Acceptance, registration, bringing to the performers, execution, control.
Naturally, to solve specific problems using one or another type of management, these algorithms can be changed in accordance with the specifics of a particular problem.
In the process of developing and making managerial decisions, the decision maker can apply various methods that directly or indirectly contribute to the adoption of optimal decisions according to various criteria.
In the literature on management and decision-making technology, there are various approaches to the classification of methods. In this paper, a classification is adopted according to the degree of formalization: non-formalized, formalized and combined. The criterion for referring to a particular group is the use of quantitative methods of information.
Non-formalized (heuristic methods) of decision making are distinguished by a creative approach to finding alternatives; they are based on the analytical abilities of the decision maker.
The advantage of informal methods is that they are applied quickly. The disadvantage is that the methods do not always guarantee the choice of error-free solutions; intuition can also fail the manager.
Figure 1.8 shows the characteristics of a sample of non-formalized methods for developing management decisions.

Rice. 1.8. Non-formalized methods of making managerial decisions
Gordon method. The essence of the method: the formation of a working group of non-specialists on the problem under consideration. Purpose and conditions of application of the method: to overcome the established ideas in solving the problem under consideration. Features of the method: use non-traditional approaches in solving the problem.
Method of motivational research. Essence: the most important type of marketing research (mainly qualitative), which consists in studying the motives for buying a certain product / service at the unconscious, subconscious and conscious levels of the buyer's psyche. The purpose and conditions for applying the method: to improve the company's marketing policy in order to increase demand for goods / services.
Method of morphological analysis. Essence: possible combinations of solving the problem are identified and then studied. A morphological matrix can be used, where solutions are located by sinks, and elements of the problem itself are arranged by columns.
consumer expectation model. Essence: the model is a forecast based on the results of a survey of the organization's customers. They are asked to assess their own future needs as well as their new requirements. By collecting all the data obtained, the manager can accurately predict aggregate demand.
Method round table. Essence: in accordance with the method, a special commission, which is part of this round table, discusses relevant issues in order to harmonize opinions and develop a unanimous opinion.
inventory method. Essence: compiling a list of difficulties that stand in the way of solving this problem, discussing options for eliminating or overcoming barriers in making and implementing a decision.
The formalized methods for developing solutions are based on a scientific and practical approach that offers the choice of optimal solutions using EMMM and computers. This can also include statistical methods, they are based on the use of information about the past experience of the organization in any field of activity for development and implementation and are implemented by collecting, processing and analyzing statistical materials both obtained as a result of real activity and artificially developed by mathematical methods. computer simulation.
balance method. Essence: a method that allows you to make balance comparisons, linkages. For example, revenues and expenses, costs and profits are compared, and the most profitable option is selected.
Histogram method. Meaning: an illustration of the frequency of occurrence of individual parameter values appears in the form of a histogram. It shows (along the ordinate) for each parameter value (horizontally) the number of corresponding cases or their share in the total number of cases. The histogram shows the frequency of occurrence of average values. Can be chosen different variants solutions, but more often the most probable ones are chosen.
Game theory method. The essence of the method: assessment of the impact of the decision on competitors. Purpose and conditions for applying the method: it is used to determine the most important factors that need to be taken into account in a decision-making situation in a competitive environment. Features of the method: it is not used so often due to the complexity and dynamism of the external environment.
Factor analysis method. Essence: the analysis allows for the maximum possible consideration of the totality of variables that characterize the object and the relationship between them. At the same time, the forecaster is forced to seek a compromise between the number of variables in the description, which reflects the completeness of the forecast, and its complexity, labor intensity.
Functional cost analysis method. The essence of the method: identifying areas of imbalance between the functions of the object and the costs of them. Purpose and conditions of application of the method: used to select solutions and optimize the costs of performing the functions of an object without compromising their quality. Features of the method: has a high practical usefulness.
IDEF modeling method. The essence of the method: analysis and development of systems. Purpose and conditions for applying the method: it is used for modeling and analyzing the activities of enterprises, as it provides a rich set of opportunities for reengineering business processes. Features of the method: the method is based on the technology of structured analysis and development.
Combined methods for developing management decisions combine elements of non-formalized and formalized methods, shown in Figure 1.11.
SWOT analysis method. Essence: SWOT methodology analysis involves establishing strong and weaknesses the internal environment of the organization, as well as identifying opportunities and threats to its external environment. Establishing chains of links between these parameters allows you to develop strategic directions (goals) for the development of the organization.
Delphi method. Essence: analysis of the situation by generating ideas, discussing them, evaluating and developing a collective point of view. Purpose and conditions for the application of methods: used to discuss the problem that has arisen and to establish the main factors that determine its further development. Features of the method: high requirements for the level of qualification and competence of the leader who leads the meeting of experts.
Decision tree method. Essence: This is a schematic representation of a decision problem. Like the payoff matrix, the decision tree gives the manager the opportunity to “take into account different courses of action, relate financial results to them, adjust them according to the probability assigned to them, and then compare alternatives.” The concept of expected value is an integral part of the decision tree method.
Brainstorming method. Essence: This method is the most well-known of all group methods of using creativity. Brainstorming is applicable to a very wide range of problems. However, it is especially useful in diagnosing situations and suggesting alternatives. The main stages of applying the method of "brainstorming":
1. A small group is formed for work, preferably no more than eight people; 2. A chairman is selected to coordinate the activities of the group. The task of the secretary is to ensure that all ideas put forward are registered; 3. All members of the group become familiar with the situation; 4. The leader of the group gives a brief comment and communicates the purpose of the work; 5. As a result of individual work, group members put forward the maximum number of ideas in a limited time (usually half an hour); 6. All ideas must be registered; 7. Encouraged to use (not copy) the ideas of other members of the group; 8. Discussion or criticism of the ideas put forward is not allowed. This rule is especially important in brainstorming situations where it is very easy to show disapproval verbally or non-verbal means; 9. After the completion of the stage of putting forward alternatives, they are discussed and evaluated. At the same time, it is possible to put forward new ideas, which can be combinations, generalizations of previously put forward ideas, or completely new ideas.
The method is nominally group. Essence It differs from other group methods in that the stage of evaluation of individually put forward ideas is regulated in more detail. The nominal group method includes the following main stages.
1. Members create independent lists of ideas; 2. Each member of the group describes one of his ideas to the whole group; 3. Once all ideas are listed, they are discussed and evaluated by the group; 4. To reach a final decision, the members of the group vote separately for each of the ideas put forward.
Method of multi-stage survey. Essence: when using the multi-stage survey method, each expert should give an assessment on a predetermined scale in the interval, or arrange the objects by decreasing their value - ordinal ordering of any set of elements. To obtain a high-quality forecast, the participants of the examination are subject to a number of requirements:
High level of general erudition;
Deep specialized knowledge;
The presence of scientific interest in the object under study in the absence of material interest in this area;
Research experience in this area.
An important element is the anonymity of experts. It helps to avoid "pressure of authority", the emergence of interpersonal conflicts based on differences in status or social coloring of opinions.
Forced connection method. Essence: This method is based on the connection of ideas, but the degree of freedom is limited by the objects in question, which are usually chosen arbitrarily. Often the participants in the discussion turn to areas that they have never considered before. Forced linking is especially useful in situations where new uses are being sought for existing products or services.
Payment matrix method. The essence of the method: evaluation and comparison of alternatives according to several criteria. Purpose and conditions for the application of the method: in the conditions of the need to take into account several parameters when evaluating alternatives. Features of the method: the validity of the choice of criteria for achieving strategic goals is important.
So, the values of the decision will remain only good wishes if they are not translated into concrete actions. Methods can be generic, suitable for any problem, and can be specific. Which method to apply depends on the real content of the problem, and not on the knowledge, desire and ability of the manager or employee. It is better not to start a business at all than to accept unprofitable, and even unlawful methods, only on the grounds that they are well known, convenient, or suit someone.
So, for successful problem solving:
Firstly, to notice and analyze the problem in a timely manner in order to find out what led to its occurrence, and in fact strive to solve it.
Secondly, do not waste time on unnecessary decisions that do not affect the efficiency of the company.
Thirdly, constantly evaluate the effectiveness of the decision-making process, and subsequently the implementation of the decision.
Fourth, do not make multiple decisions on the same issue.
Fifthly, to involve employees related to them in the decision-making process already at the earliest stages of work, taking into account the correspondence of their qualifications to the degree of complexity of the problem; educate them as needed and don't forget to reward them for their success.
Decision-making technology is a set of scientific methods, models and techniques for developing and making managerial decisions.
Chapter 2
2.1 Characteristics of the enterprise and the mechanism for making managerial decisions at the enterprise CJSC "VNESHTORGSIB - M"
CJSC Firm Vneshtorgsib-M has been operating on the Russian market since 1993. Since its foundation, the company has focused on the supply and trade of imported goods.
The firm "Vneshtorgsib - M" is official representative the German trade mark "PAPSTAR" is the only large-scale project of goods for a cozy interior, a festive table, a cocktail and buffet, picnics and holidays, an aromatic line in Russia.
The goals of the creation of the society are: meeting the needs of individuals and legal entities in products (works, services) produced by the Company; Receiving a profit.
The mission of CJSC "Vneshtorgsib - M" is to meet the demand of customers by providing them with quality and related products at affordable prices.
CJSC "Vneshtorgsib - M" currently has the following divisions:
1.Wholesale base
2. Administration, located on the street. Kotovskogo 5
3. Shop "Gifts" on the street. Ordzhonikidze 27
4. Shop "Gifts" on the street. Kotovskogo 5
5. Shopping mall"Podmoskovye" opened in July 2006, the format of the cash-and-carry shopping center.
6 Dedicated station for renting and renting "Hobby" brand trailers, Germany and "Hymer" caravans,
Germany, trailers-tents brand "Camp-Let", Denmark, as well as their repair. Works since June 2007.
Figure 2.12 shows the share of activities of CJSC Vneshtorgsib-M in the total volume.

Figure 2.12 The share of activities of CJSC Vneshtorgsib-M in the total
Positive advantages in terms of internal resources are the following features:
The company has a high level of professionalism, which is important, as well as the desire of consumers to have an unlimited choice in the goods and services presented to them.
A positive factor is the presence of a developed logistics infrastructure, which allows you to plan stocks, make deliveries just in time.
The enterprise has implemented a partially integrated automation of business processes, automation of business management operations in accounting departments and stores, which allows making operational management decisions and adequately responding to market changes, a unified document flow has been implemented that speeds up business operations.
The range of the enterprise under study is presented by the following product groups in table 2.2:
Table 2.2 The range of goods presented in the subdivisions of CJSC Vneshtorgsib - M
A lot of attention is paid to the assortment formation policy at the enterprise under study - a constant assessment of the completeness and stability of the assortment is carried out.
When forming the assortment, the financial director of CJSC Vneshtorgsib-M focuses on the demand of end consumers of products. CJSC "Vneshtorgsib - M" strives to fully satisfy the needs of customers.
In order to intensify and stimulate sales, ZAO Vneshtorgsib-M uses advertising and public relations. The advertising spend limit is currently capped at 3% of revenue generated.
The main goal that is recommended to be pursued by CJSC Vneshtorgsib-M when organizing its own work can be reduced to the following: to help ensure that the company's advertising policy meets the consumer needs of potential buyers.
The organizational structure is presented in more detail in Annex 1.
The function of the head office is to direct activities and control, the entire decision-making process is concentrated in the head office.
In accordance with the current functional structure of enterprise management, the following composition of the main functions and services that ensure their implementation is approved, see Appendix 2 in more detail:
· CEO
Involved specialists – lawyer, translator, technical staff, security service.
financial department - financial director, finance manager;
accounting - chief accountant, accountant, senior cashier;
personnel department - head of the personnel department - clerk;
trade department - commercial director; deputy commercial director; wholesale manager, retail manager
Stores – division directors, section heads, senior salesperson, sales consultants
· Wholesale depot – director, merchandiser, sales consultant, driver, mechanics.
So let's give brief description functional duties company employees and departments.
General Director - he is at the head of the company, without a power of attorney represents on behalf of the Company; represents the interests of the Company in all Russian and foreign institutions, enterprises and organizations; enters into transactions on behalf of the company, with the exception of those, the conclusion of which is within the competence of the general meeting of shareholders, the Board of Directors and the Management Board of the Company; enters into labor agreements (contracts) with employees of the Company, with the exception of members of the Board of the Company; issues powers of attorney; issues orders and instructions binding on all employees of the Company.
The financial director is the right hand of the commercial director, develops the marketing policy at the enterprise based on the analysis consumer properties products sold and predicts market demand and market conditions.
The commercial director - this person on the scale of this company performs a large number of functions that were very interesting to me, as the future manager of the organization. Since the entire burden of the direct process of managing the movement of goods, compiling primary documentation, work with personnel (managers), organization and holding of meetings and presentations. And also, drafting commercial offers, managing money spent on advertising campaigns, business correspondence, etc.
Table 2.3 Functional structure of ZAO Vneshtorgsib-M
| Job title | Functions |
| Translator | Helps in negotiating with foreign companies, makes a transfer to the goods. |
| Lawyer - consultant | Development of legal documents, legal assistance to structural divisions of the company (shops) in preparing responses to claims. |
| Financial department | Carries out the development financial policy at the enterprise based on the analysis of consumer properties of the products sold and predicts market demand and market conditions. The department organizes the development of a strategy for conducting promotional activities in the media with the help of outdoor, illuminated, electronic, postal advertising, advertising on transport. |
| Accounting | The department maintains the organization's records required for both internal management purposes and for presentation to external users. The accountant reports to the CEO on the basis of the annual report, and submits a report on financial results. The director makes decisions on the results of the enterprise, decides on the target distribution of profits, the amount of funds, reserves. |
| Human Resources Department | Manages the work of staffing the enterprise with workers and employees of the required professions, specialties and qualifications in accordance with the goals, strategy, and profile of the organization, changing external and internal conditions of its activities. Ensures the preparation of documents for pension insurance, as well as documents necessary for the appointment of pensions company employees and their families. |
| Information technology department | Competent and accurate writing of new codes and names of goods, processing of documents in a single database. Correspondence with foreign partners. |
| Sales Department | Carries out activities for the supply and sale of products in order to increase the profits of the enterprise; plans and analyzes sales, takes measures to increase turnover; develops and implements measures to compensate for the decline in sales for seasonal groups of goods. Draws up contractual relations, orders goods, monitors underdeliveries and re-grading of goods; timely notifies suppliers about regrading and non-delivery of goods, requests certificates; makes an analysis of seasonal, calendar and other factors affecting fluctuations in demand. |
| Wholesale base | Carries out activities for the supply of products to the retail departments of the organization. Works with large wholesalers, by bank transfer. |
| The shops | They carry out activities for the sale of goods at retail, and work with small wholesale buyers. |
So, on this enterprise there is a functional principle of construction and specialization of the management process according to the functional subsystems of the organization. The functions of the head office of Vneshtorgsib-M are to direct and control activities, the entire decision-making process is concentrated in the head office. In CJSC "Vneshtorgsib - M" the final result recedes into the background, due to the fact that each service does not work to obtain it, but to fulfill its "mechanical" duties.
To increase the competitiveness of the enterprise ZAO Vneshtorgsib-M, it is important to have clearly defined and set goals and objectives, since it is a well-set goal that will affect the efficiency of the enterprise. It is also necessary that each division of the enterprise set a specific goal for itself, which, together with others, will help achieve a common goal. To achieve the goals of the enterprise, each department performs the appropriate tasks, respectively, the tasks also play a significant role in the internal structure of the enterprise.
The existing technology of making and executing decisions does not allow to bring the tasks of the upper level (profit, sales, saving resources) to all the lower divisions.
2.2 The process of making managerial decisions at the enterprise CJSC "VNESHTORGSIB - M"
Management decision-making is based on certain documentation. All documents that circulate in the document management system, CJSC "Vneshtorgsib - M" are divided as follows and are presented in Appendix 3.
The decision-making process is reflected in all aspects of management. Management activities in terms of the formation and implementation of decisions at the enterprise CJSC "Vneshtorgsib - M" consists of the following stages:
1. Preparation of a management decision
2. Providing procedures for making and making a management decision
3. Implementation of a management decision
4.Planning management decision
5. Control over the implementation of the solution
Table 2.4 Distribution of powers at the stages of decision-making technology in CJSC Vneshtorgsib-M
As can be seen from the stages of the process, managerial decision-making is highly dependent on the personal factor, since in fact decisions in the company are made by only one person, the general director.
With the help of the management matrix, one can illustrate the level of distribution of powers in making managerial decisions in an enterprise.
"1" indicates the actual responsibility.
"2" - general guidance.
"3" - the need to consult.
"4" - "opportunity" to consult.
"5" - must be notified
Table. 2.5 Distribution of powers in decision-making
| Director | Inform. Department | Fin. Department | Accounting | Personnel department | Sales Department | Subdivisions | |
| Activity planning | 1 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 5 |
| Conducting performance analysis | 1 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 5 |
| financial planning | 2 | 5 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Accounting | 2 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 3 |
| Marketing planning | 1 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 5 |
| Supplying the company with goods | 2 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
| Documentation of trade and technological operations | 1 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 5 |
| Human resource management | 1 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 4 |
We will assess the level of decision-making using a 5-point system (see Table 2.6).
Table 2.6 Evaluation of the level of decision-making by the personnel of the enterprise
| Decision maker | Decision quality assessment | Explanations |
| Director | 3 | Too authoritarian decisions, rarely uses the opinions of other specialists |
| Chief Accountant | 3 | |
| CFO | 4 | |
| Commercial Director | 4 | Attempts to be creative are manifested, limited by the power of the director |
| Head of Human Resources (clerk) | 3 | Solutions are formulaic, based on the instructions of the CEO |
| Division directors | 3 | Solutions are template, does not consider other alternatives and possibilities |
| sales staff | 3 | They do not show independence, rely on the instructions of the general director, director of departments |
So, as can be seen from the process of making managerial decisions, decision makers partially show attempts at a creative approach, but basically the whole process is implemented on the implementation of a specific decision set by the general director. The decision-making management process in ZAO Vneshtorgsib-M is authoritarian. The adoption of managerial decisions strongly depends on the personal factor, since in fact decisions in the company CJSC "Vneshtorgsib - M" are made by only one person - the general director
There is no informing of the personnel about the current results of the enterprise's activity, employees are informed about the changes taking place after the fact.
2.3 Typical problems of the enterprise CJSC "VNESHTORGSIB - M"
The inefficiency of the existing decision-making mechanism at the enterprise ZAO Vneshtorgsib-M is evidenced by the fact that the enterprise has an outdated management system.
The retail industry plays a big role in our lives. Therefore, retailers are commercial organizations that sell goods and services to the consumer for personal and household consumption. Retailers provide goods and services only by the piece, their customers are end users who buy goods and services for personal use and not for resale to third parties.
Like a service industry retail must rely on its employees to represent stores to the consumer, creating important points of contact with them. Therefore, personnel costs should be one of the most important expense items in the industry. However, the retail industry has a poor reputation as a job creator. Retailers must provide services to people when they really need them, which increases the length of the working day and work week in the industry.
Accordingly, one of the problems of CJSC Vneshtorgsib-M is the lack of qualified sales personnel. The company constantly has a turnover of salespeople - consultants, so after the new year, four salespeople quit at once.
In the course of the work, an oral survey of employees of the organization under study was conducted. 26 out of 36 employees were interviewed.
Let's analyze the received information.
Size wages.
80% of respondents noted average satisfaction with the size of wages. It is necessary to increase material incentives for employees by raising wages or organizing a system of bonuses and bonuses to raise the indicator.
Prospects for professional and career growth.
The survey showed that more than half of the employees do not see growth prospects in this organization.
Management should take a greater interest in the growth and progress of employees. This can be expressed in the fact that the employee will be entrusted with more complex work, you can delegate more responsibility to the employee for the performance of certain work.
Relationship with immediate supervisor.
80% of the respondents answered that they were not satisfied with this indicator.
The importance and responsibility of the work performed.
Only 40% of the surveyed workers meet this indicator. This is due to the small number of staff. It is important to understand that the mistake of even one employee can affect the financial position of the company.
Relationships with co-workers.
60% of the respondents answered that they were quite satisfied with this indicator. In the future, the organization should implement measures aimed at maintaining good relationships between employees.
Opportunities for independence and initiative in work.
All respondents answered that they were not satisfied with this indicator. The General Director of CJSC "Vneshtorgsib - M" should be given more initiative in the duties performed by employees.
CJSC "Vneshtorgsib - M" still manages to compete to some extent with large firms and federal operators, due to the ability to set low prices, being an official representative, due to the high quality of goods and shops located in the city center. And keep your market niche.
Important for the formalization of expert information is the ability of an expert to compare and evaluate the possible values of the features of the object of analysis by assigning a certain number to each feature. Depending on the scale on which these preferences are set, expert assessments contain more or less information.
In the general case, it is assumed that the opinion of a group of experts is more reliable than the opinion of an individual, i.e. that two groups of equally competent experts are more likely to give similar answers to a set of questions than two individuals.
The experts were asked to assess the strengths and weaknesses of the enterprise. Experts at the first stage of the analysis assessed the weight of each of the listed parameters for the industry. The parameter weight characterizes its importance, priority, in the total set of indicators.
Table 2.7 Analysis of strengths and weaknesses of ZAO Vneshtorgsib-M
Components of the internal environment |
The effectiveness of the components of the environment | Importance | |||||||
| neutral | |||||||||
| Marketing: | |||||||||
| Reputation of the organization and products | – | – | + | – | – | + | – | – | |
| Market share | + | + | |||||||
| Goods quality | + | – | – | – | – | + | – | – | |
| Production costs | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | – | |
| Distribution costs | – | – | – | + | – | – | + | ||
| Promotion efficiency | – | – | + | – | – | + | – | – | |
| Sales performance | – | – | – | – | – | + | – | ||
| Finance: | – | ||||||||
| Financial stability | – | – | – | + | – | – | – | – | |
| Debt | – | – | + | – | – | + | – | ||
| Inventory level | – | – | + | – | – | + | – | ||
| share price | – | – | + | – | – | + | – | – | |
| Level of innovation | – | – | + | – | – | + | – | – | |
| Financial Accounting | – | – | – | + | – | + | – | – | |
| Organization and personnel: | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | ||
| Entrepreneurial Orientation | - | - | + | – | – | + | + | – | |
| Management organization level | – | – | + | – | – | - | + | – | |
| Leadership Qualification | – | – | + | – | – | + | – | – | |
| Personnel qualification | – | – | – | + | – | + | – | – | |
| Rational distribution of rights and responsibilities | – | – | – | + | + | – | + | - | |
| System of values: | |||||||||
| Presence of traditions, symbols, rituals | – | – | + | – | – | + | – | – | |
| Motivation system | – | – | – | + | – | + | – | – | |
| Psychological climate in the team | – | – | – | + | + | – | – | ||
The external environment is of exceptional importance for commercial enterprises. To present it, we will briefly characterize the main parameters of the external environment, which also affect the enterprise ZAO Vneshtorgsib - M (Table 2.8).
Table 2.8 The external environment of the enterprise CJSC Vneshtorgsib - M
| Macroenvironment |
The tax burden is large and does not allow business to develop actively High customs duties, registration and market licensing Inflation is on the rise The political situation in the country has stabilized There are many unemployed in society, including in the industry Constantly improving quality characteristics |
| Immediate environment |
Inability to maintain the matrix of goods imported from Europe due to the constant change in the assortment by manufacturers Buyers are price sensitive Income growth of the population and firms The time schedule for the delivery of goods is determined depending on the type of product and ranges from one to several months. Entry into the market of competitors with lower costs |
Using the matrix "importance of efficiency" in the table, according to the results of the analysis, we will compile the highest and lowest importance, which is worth paying attention to (Table 2.9)
Table 2.9 Importance-Effectiveness Matrix
| Importance | Efficiency | |
| low | high | |
| high | Requires special attention Production costs; Distribution costs; financial instability; Motivation system; Psychological climate in the team. |
Maintains a high level Product quality; Availability of exclusive products; Long-term contracts with key exporters |
| low | Low priority Reducing the crime situation in the country; Customs legislation remains unchanged; Lack of managerial training of a number of managers. |
Overemphasis on unimportant factors Entrepreneurial Orientation Changing needs and tastes of customers |
So, the level of decision-making at the enterprise is low, this is reflected in its financial condition. Need to improve financial results, increase the market share and efficiency of the management system as a whole. To do this, first of all, the enterprise needs to improve the system of development and decision-making.
Chapter 3
It is recommended to the enterprise "Vneshtorgsib-M": - to implement in management the decision-making algorithm for situational management, described in clause 1.3; - allocate responsibility for collecting and analyzing information about the situation; - involve employees of the company in decision-making, with the provision of greater powers to them; - decision-making to carry out with the help of various methods of management decision-making technology. We will illustrate the application of these measures by evaluating the increase in the efficiency of financial accounting.
3.1 Efficiency of management decisions in ZAO Vneshtorgsib-M
Evaluation of the effectiveness of a management decision is determined not only by its validity, but also by the degree of its implementation in accordance with the requirements of the decision maker.
Efficiency comes from the word "effect", meaning the impression made by someone on someone. This impression can have organizational, economic, psychological, legal, ethical, technological and social overtones. The effect can be observed or formed.
Management of the effectiveness of a management decision is implemented through a system of quantitative and qualitative indicators, norms and quality standards.
The efficiency of the trading enterprise is ensured by the successful implementation of services. The resources of the enterprise and the requirements of cost-effective work to a certain extent limit the maneuvering, both in the range of services and in the prices for them. But it is the focus on customer demand and its active formation that should determine the use of available resources.
The ratio of the result and costs characterizes the effectiveness of any activity or phenomenon. It can be positive or negative. Thus, we can talk about organizational, economic and other efficiency.
In our case, we will talk about the effectiveness of financial results.
Trading activities of CJSC "Vneshtorgsib-M" are divided into main and management and auxiliary. The main activity involves the sale of goods, works and services. Auxiliary, performs repairs and reconstruction, construction of buildings, structures; repair of official vehicles, supply of materials necessary for the operation of the enterprise, etc. The manager performs regulatory and supervisory functions.
Let's focus on the main trading activity and consider the dynamics of changes in trade turnover in the table over the past four years.
Table 3.10 Changes in the turnover of the company CJSC "Vneshtorgsib-M"
| Indicator, thousand rubles | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Trade turnover | 111945 | 134577 | 162111 | 195395 |
| 1 quarter | 17962 | 47652 | 26979 | 25296 |
| special services station | - | - | - | 6659 |
| 2 quarter | 26744 | 59911 | 43189 | 47200 |
| special services station | - | - | - | 9100 |
| 3 quarter | 29784 | 13572 | 45374 | 41617 |
| special services station | - | - | - | 9600 |
| 4 quarter | 37456 | 44214 | 46570 | 45783 |
| special services station | - | - | - | 10140 |
| Costs including: | 109480 | 133494 | 162038 | 196143 |
| - cost of goods | 43423 | 51167 | 61400 | 74035 |
| - materials used in the repair | - | - | - | 12166 |
| - rent and utility bills | 6030 | 6210 | 6320 | 7125 |
| - administrative | 4250 | 7145 | 9560 | 8956 |
| - remuneration of employees | 29545 | 32457 | 34120 | 43652 |
| - taxes | 9548 | 9231 | 10250 | 12511 |
| - nutrition | 2103 | 2468 | 2576 | 2874 |
| - acquisition of fixed assets | 487 | 1644 | 3674 | 2548 |
| - communication, information services | 316 | 531 | 562 | 463 |
| - vehicle maintenance | 1023 | 1455 | 1987 | 2145 |
| - general trade | 855 | 1520 | 1987 | 2650 |
| - technological costs | 1020 | 1999 | 2630 | 2880 |
| - transportation of goods | 3567 | 3658 | 5012 | 4950 |
| - general business needs | 410 | 623 | 755 | 987 |
| - construction | 6903 | 13386 | 21205 | 18201 |
| Financial results | 2465 | 1083 | 73 | -748 |
Considering the dynamics of sales, we note that the main demand for goods and services offered to the consumer falls on the second, third and fourth quarters of the year. The seasonality of demand for products is very important. Comparing four years, we note that every year there is an increase in trade by about 20 percent. This is due to the opening of the Kotovsky store in 2005, the Moscow Region store in 2006, and a specialized station on Chasovaya in 2007. In 2004, the territory was purchased, where the construction of a specialized station began and continues to this day. In this regard, in the next three years, the costs of the enterprise increased to the maximum for: the maintenance of additionally attracted workers; acquisition building materials and TMC; fixed assets. From the table you can see a stable increase in costs: in 2005 compared to 2004 they increased by 21.9%; in 2006 compared to 2005 by 21.4%; in 2007 by 21%, and compared to 2004 - by 79.2%. The diagram and graph of changes in income and expenses are shown in Figure 3.15, respectively.

Fig.3.15. Diagram of changes in income and expenses

Fig.3.16. Schedule of changes in income and expenses
According to the diagram, it is convenient to study the change in income and expenses for four years. Studying the chart, you can immediately pay attention to the point of intersection of income and expense. At this point, the company is on the verge of profit or loss. In connection with the expansion of activities, there was a need to increase the staff, so from 2004 to 2007 the number of employees increased from 42 to 70 people, which led to an increase in the payroll compared to 2004 by 47.7 percent.
With the increase in turnover, the cost of transporting goods increased by 38.7%.
Significant funds were required for the construction of the station. The company's own funds, which remained from retained earnings, were not enough, in connection with this, credit resources were attracted, the interest on which increased the item "administrative expenses" by almost 100 percent.
Administrative expenses also increased due to: recruitment costs, security services, legal services (documentation).
Rent, utility bills, communications, information services, and general business needs have not changed significantly in four years.
Although the turnover also increased compared to 2004 - by 74.5%, it can be concluded that the management staff, headed by the general, financial director and chief accountant, did not track the growth of costs, did not take measures to minimize them. This led to a deplorable result: by the beginning of 2007, the profit was replaced by a loss (748 thousand rubles). Also, wage arrears increased by 12,132.
For further analysis and management of costs, it is advisable to classify them into variable and fixed.
Variables:
Cost of goods;
Transportation of goods;
Materials used in the repair;
Remuneration of employees;
international negotiations;
Technological costs.
Permanent:
Rent and utility payments;
Administrative;
Nutrition;
Acquisition of fixed assets;
Communication, information services;
General business needs.
So, evaluating the effectiveness of the implementation of decisions is the most complex, time-consuming and lengthy stage of the decision-making process. At the same time, this is also the weakest link in the process of managerial activity, as evidenced by the delay in the implementation deadlines observed in management practice and the insufficient effectiveness of implemented decisions.
In the company's activities, a necessary condition for effective functioning is the balance of interests of all business participants (owners, managers, staff, counterparties, customers, etc.).
The enterprise is considered quite large in terms of turnover, but the organization of activities is at the level of a small enterprise and at present management accounting as such is not provided. In the next, we will try to organize management accounting, primarily by identifying centers of financial responsibility and introducing budget management.
To implement the management accounting subsystem, it was necessary to conduct a business diagnostic (a kind of "inventory") of the company. In the process of business diagnostics, the current state of the company's structure and management system is assessed and the effectiveness of the existing financial planning and control system is analyzed in terms of completeness, reliability and efficiency of information provision. An assessment of the current state of the management system in CJSC Vneshtorgsib-M was carried out at the beginning of this chapter, on the basis of which a decision was made to introduce management accounting.
After the diagnostics, the concept of creation is developed financial system. The goals, objectives and principles of its construction, the composition and structure of the system (financial responsibility centers, forms of regulations) are determined. The description of the processes of planning, control and analysis is carried out. Then the order of development, implementation and maintenance of the system is determined. The action plan for the implementation of management accounting is presented below. Action plan for the implementation of management accounting
Stage 1. Preliminary
a) Analysis financial condition organizations to justify the need to introduce management accounting
b) Definition of goals, objectives and principles for building the structure of the management system
2) Stage. Organizational
a) Development of a policy for the introduction of management accounting
b) Formation of financial responsibility centers
c) Training activities for department managers
3) Stage. Basic
a) Setting deadlines for submitting budgets for consideration and approval
b) Development of the form and formation of budgets by cost and profit centers
c) Formation of consolidated and general budgets
d) Implementation of a budget management system based on the 1C program
4) Stage. controlling
a) Implementation of a system for monitoring the costs incurred by the economic group
b) Quarterly meetings following the results of the reporting period
The implementation of the financial system goes in two directions:
The main budget of the company is developed, which is a system of integrated budget planning all activities and depends on business processes;
· budgets of structural subdivisions and consolidated budgets are built, the composition of which depends on the organizational structure of the company.
At the end of the year, before December 15, each division submits its quarterly budget for the next year to management for consideration. Until the 25th, a commission composed of the General Director, financial director, chief accountant and directors of departments, approve the budget for the next reporting period.
When building a financial system, it is necessary to provide and build a system for monitoring the implementation of budgets. It consists not only in the timely presentation of budget data and the creation of budgets, but also in the analysis of deviations of the actual values of budget items from the planned ones. Based on the analysis of deviations, appropriate management decisions are made.
Let's consider an example of analysis of actual results. Let the income be planned for the amount of 5000.00 rubles, the expense for 4500.00 rubles, then the profit is 500.00 rubles.
1) income - 4800.00, expenses - 4200.00, profit - 600.00. In this case, the unit manager did not complete the income plan by 4%, but reduced costs by 6.7%, thereby increasing profit by 100.00 rubles (by 20%). By and large, this option can satisfy the higher management, with the condition that the manager will work on increasing profits.
2) income - 5200.00, expenses - 4800.00, profit - 400.00. The situation is reversed - income compared to the plan increased by 4%, and expenses increased by 6.7%, which led to a decrease in profit - by 100.00 rubles. Conclusion - it is necessary to introduce measures to reduce costs.
3) income - 5200.00, expenses - 4300.00, profit - 900.00. An ideal managerial job, deserving of encouragement. By increasing revenue by 4%, he reduced costs by 4.4%. And the division's profit increased by 80%.
4) income - 4800.00, expenses - 4900.00, loss - 100.00. In this case, the manager did not fulfill the income plan by 4%. A 9% increase in costs resulted in a loss. The unit needs to revise the cost item to reduce them.
Control over the expenses incurred is carried out by the head of the unit - the cost center, profit, and before paying the necessary costs, they must be endorsed by the financier, confirming that the payment went through the budget of the unit. Extrabudgetary payments are made on the basis of memo and budget adjustments.
The system of control over the execution of budgets involves holding meetings as part of the management of the enterprise and directors of departments at the end of each reporting period - a quarter, where they discuss: the causes of negative deviations in profits and costs from the budget; the need for activities to increase sales and minimize costs. At the end of each quarter, according to the positive results of the execution of budgets, the units that have fulfilled the plan are rewarded in accordance with the established bonus rates.
The budget management system can be implemented on the basis of the 1C program, which will make it possible to monitor the execution of the budget on a daily basis, both by individual departments and by the enterprise as a whole.
Main working capital the company sends to pay for the goods. In this regard, the problem of monitoring the timeliness of payment and compliance with the terms of contractual conditions is very important. In order to be able to control payments to suppliers, it is necessary to develop a payment planning form, which will show not only the total debt, contractual payment terms, overdue debts and the cost of inventory, but also the turnover by supplier. All this information will allow you to evaluate the effectiveness of working with a particular supplier, and provide automatic control over the terms of payment, which will lead to control over the cost of production. In CJSC "Vneshtorgsib - M" carried out on the basis of data accounting analysis of the dynamics of development of retail trade in 2004-2007. allows us to draw the following conclusions:
· Retail trade turnover of CJSC “Vneshtorgsib-M” is increasing from year to year, its growth rates are high;
· reached the growth of turnover for all commodity groups, which are traded by the company;
· the increase in trade turnover, mainly achieved through the effective use of all types of resources: commodity, labor, etc.;
· In 2007, the company was actively working on additional purchases of goods from the manufacturer and other suppliers.
At the same time, the ZAO Vneshtorgsib-M enterprise did not use all the opportunities for increasing the turnover in 2004-2007. Thus, the volume of retail trade could increase due to:
· improving the availability and efficiency of the use of commodity resources;
· increase: the efficiency of the use of labor resources;
increasing the efficiency of using the material and technical base of the company. The search for new suppliers and, as a result, an increase in the range of goods will allow CJSC Vneshtorgsib-M to reduce the impact of the seasonal factor on the change in turnover.
The calculation of seasonal fluctuations in the turnover of the enterprise under study is given in table 3.11.
Table 3.11 Calculation of seasonal fluctuations in the turnover of ZAO Vneshtorgsib-M (thousand rubles)
| Year | Average turnover of the same months |
Seasonality index (column 6: total tr, 6) |
||||
| 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | Total | |||
| January | 425 | 440 | 450 | 1315 | 438,3 | 0,95 |
| February | 420 | 460 | 470 | 1350 | 450 | 0,980 |
| March | 480 | 560 | 580 | 1620 | 540 | 1,172 |
| April | 460 | 530 | 540 | 1530 | 510 | 1,107 |
| May | 445 | 480 | 500 | 1425 | 475 | 1,031 |
| June | 420 | 425 | 430 | 1275 | 425 | 0,922 |
| July | 415 | 420 | 425 | 1260 | 420 | 0,911 |
| August | 415 | 405 | 425 | 1245 | 415 | 0,901 |
| September | 450 | 430 | 440 | 1320 | 440 | 0,955 |
| October | 460 | 440 | 470 | 1370 | 456,7 | 0,991 |
| November | 400 | 440 | 560 | 1400 | 466,7 | 1,013 |
| December | 430 | 450 | 600 | 1480 | 493,3 | 1,070 |
| Total | 5220 | 5480 | 5890 | 16 590 | 460,8 (16 590:36) | 1,000 |
The volume of turnover for the planned year by months is determined by multiplying the average monthly plan of turnover by the seasonality index.
The company's turnover plan for the year is set at 24 million rubles. The average monthly turnover is 2 million rubles. Using the data in the table, we calculate the store's turnover plan for March. It will be: 2 million rubles. * 1.172 = 2344 thousand rubles
The final stage of planning is the determination of the commodity structure of the turnover. The extent to which the range of goods sold will meet the demand of the population largely depends on the financial result of the enterprise. For traditional groups of goods, in practice, the economic and statistical method has proven itself well, when, based on the current rate of change in sales of individual product groups, adjusted for expected changes in the economic development of the enterprise in the coming period, a plan for their implementation is established.
Proposals for the further development of the retail trade turnover of CJSC Vneshtorgsib-M: to improve the company's commodity supply and increase the efficiency and use of commodity resources. To this end, the commercial service of the enterprise should significantly expand the purchase and sale of related products (for example, the sale of decorative lamps), which are available in sufficient quantities from manufacturers and other suppliers, and pay more attention to concluding contracts with suppliers.
An increase in commodity resources will make it possible to obtain an increase in trade turnover, to achieve an increase in the efficiency of the labor of sales workers.
To this end, it is advisable to employ persons on a part-time basis, to install modern cash registers, carry out a combination of professions, positions, work to prevent absenteeism and reduce loss of working time due to illness and other reasons.
Improving the use of the material and technical base of the enterprise.
To this end, to establish the optimal mode of operation of the enterprise, to introduce progressive forms of trade, to reduce to a minimum the conduct of inventories, inspections, the economic service of the enterprise to develop forecasts for the development of retail trade for the coming period and conduct operational monitoring of the implementation of forecasts;
This will allow the management of Vneshtorgsib-M CJSC and its services to promptly resolve issues of ensuring and efficient use of all types of resources, to achieve a rhythmic and uniform development of retail trade turnover by periods of the year and by departments of the enterprise.
Necessary:
Improve the system of material incentives for the work of company employees (increasing the number of goods sold, serving the largest number of customers, receiving income from the sale of goods, etc.);
introduce a journal-order form of accounting at the enterprise, more quickly present data on retail for making managerial decisions;
Implement computerization of management accounting at the enterprise, use a reference computer system for consultations, clarifications, etc.
Thus, due to the developed management decision, the enterprise can actually achieve its goals and increase the overall performance indicator, reduce production costs.
So, improving the process of making managerial decisions and, accordingly, improving the quality of decisions made is achieved through the use of a scientific approach, models and methods of decision-making.
Conclusion
Improving the process of making managerial decisions and, accordingly, improving the quality of decisions made is achieved through the use of a scientific approach, models and methods of decision making. The goals set in the introduction, in my opinion, are disclosed in the work. Summing up, some conclusions can be noted.
A decision is a choice of an alternative. The need for decision-making is explained by the conscious and purposeful nature of human activity, it occurs at all stages of the management process and is part of any management function.
Decision-making (management) in organizations has a number of differences from the choice of an individual, since it is not an individual, but a group process.
The nature of the decisions made is greatly influenced by the degree of completeness and reliable information that the manager has. Depending on this, decisions can be made under conditions of certainty (deterministic decisions) and risk or uncertainty (probabilistic decisions).
The complex nature of the problems of modern management requires a comprehensive, comprehensive analysis of them, i.e. participation of a group of managers and specialists, which leads to the expansion collegiate forms decision making.
Decision-making is not a one-time act, but the result of a process that has a certain duration and structure. The decision-making process is a cyclic sequence of actions of the subject of management aimed at resolving the problems of the organization and consisting in analyzing the situation, generating alternatives, choosing the best one and implementing it.
Decision making is the most important thing in a manager's job. Therefore, it is necessary to learn how to make decisions even in the process of learning, and not when the fate of the enterprise already depends on the leader. Moreover, now you can learn not only from your own mistakes, but also from the experience of other people and organizations.
So, we have considered and characterized the decision-making process from a technological point of view. Let's summarize the results of the work:
1. A decision is a choice of an alternative, a conscious choice from the available options for a course of action.
2. A decision is a product of managerial work, and its adoption is a process leading to the emergence of this product.
3. The choice of a solution should be based on the characteristics of the problem situation.
4. Depending on the approach to the decision-making process, technologies of this process are distinguished. However, they all distinguish three main stages: defining the problem, developing a solution, and implementing the solution.
5. All responsibility for the decision is assigned to the head, manager. Currently, there are no practical, constructive methods or technologies for making group decisions or decisions in the face of opposition with many active participants. Far from being satisfactorily solved are many of the relatively simpler problems of individual decision making. Thus, the processes taking place in the administrative apparatus are much more complicated than those for which analytical approaches have already been developed. Thus, our hypothesis was confirmed. However, consideration of the problems that have arisen in a strict logical sequence makes it possible to fruitfully combine formal and heuristic methods in the process of preparing and making a decision and achieve a higher quality.
6. The work of the consultant-analyst plays a huge role and is of primary importance. Reality requires him to combine many qualities: the art of analyzing situations, deep professional knowledge, techniques and methods of decision-making, the ability to present recommendations, and professional skills in working with people.
In our opinion, in the coming decades, many so-called. behavioral sciences will definitely take a step forward. Then it will be possible to build much more efficient decision-making technologies. But already now it is necessary to consider the decision-making process as a procedure, the main participants of which are the manager and analysts. It is the human aspects, not the mathematical or machine aspects, that are central to the decision-making process. It is on these aspects that criteria for testing the practical value of technologies and decision-making methods should be based in the future.
Proposals for further development of the retail trade turnover of Vneshtorgsib-M CJSC: to improve the company's commodity supply and increase the efficiency of the use of commodity resources.
To this end, the commercial service of the enterprise should significantly expand the purchase and sale of related products (for example, the sale of decorative lamps), which are available in sufficient quantities from manufacturers and other suppliers, and pay more attention to concluding contracts with suppliers. The search for new suppliers and, as a result, an increase in the range of goods will allow CJSC Vneshtorgsib-M to reduce the impact of the seasonal factor on the change in turnover.
List of sources used
1. Brazhko E.I., Serebryakova G.V., Smirnov E.A. Management decisions: Tutorial. - M.: RIOR, 2006. - 126 p.
2. Vertakova Yu.V. Management decisions development and choice: Textbook / Yu.V.Vertakova, I.A.Kozyeva, E.N. Kuzbozhev. – M.: Knorus, 2005. – 352p.
3. Vikhansky O.S. Management: Textbook / O.S. Vikhansky, A.I. Naumov. - M.: Gardariki, 2000. - 528s.
4.Glukhov V.V. Management: Textbook for universities. 3rd ed. - St. Petersburg: Peter, 2008. - 608s.
5. Gribov V.D. Management: Textbook. – M.: Knorus, 2007. – 280s.
6. Golubkov E.P. Management decision-making technology: Textbook. - M .: Publishing house "Delo and Service", 2005. - 544 p.
7. Durdenko V.A. Development of management decisions - Voronezh: VIESU, 2004. - 177s.
8. Jurabaev K.T. Production management: Textbook for universities / K.T. Dzhurabaev, A.T.Grishin, G.K.Dzhurabaeva. – M.: Knorus, 2005. -416s.
9. Dorodnikov V.N. Fundamentals of commercial activity: Textbook - Novosibirsk: NGAEiU, 2002. - 77s.
10. Efimov V.V. Improving the quality of products, processes, resources - M .: Knorus, 2007. - 240s.
11. Jean-Jacques Lambin. Market-oriented management. - M.: Peter, 2005. - 796s.
12. Zub A.T. Strategic Management: Theory and Practice. Textbook - M .: Aspect Press, 2002. - 415s.
13. Ivasenko A.G. Development of management decisions: Textbook / A.G. Ivasenko, Ya.I. Nikonova, E.N. Plotnikova. - Novosibirsk: SSGA, 2007. -162p.
14. management notes. Handbook of the leader / ed. V.V. Kondratiev. - M .: Eksmo, 2007. - 832 p. - group of authors.
15. Kabushkin, N.I. Fundamentals of Management - 10th ed., - M .: new edition, 2007. - 336s.
16. Kent, Tony. Retail trade: Textbook for university students / T.Kent, O.Omar; per. from English - M.: Unity - Dana, 2007. -719s.
17. Kardanskaya I.L. Fundamentals of managerial decision-making: Textbook for universities - M.: Russian business literature, 1998. - 288s.
18. Kibanov A.Ya Personnel management of the organization / A.Ya. Kibanov - M .: Infra - M - 2004.- 276s.
19. Lukicheva L.I. Management decisions: A textbook on the specialty "Management of the organization". - M .: Omega - L, 2007. - 383 p.
20. Litvak B.G. Development of a management decision - M .: Infra - M, 2005. - 304 p.
21. Levi M., Weitz B.A. Fundamentals of retail trade / Per. from English; Ed. Yu.N. Kapturevsky. - St. Petersburg: Peter, 2005. - 448s.
22. Mazur I.I. Quality management / I.I. Mazur, V.D. Shapiro, 4th ed., - M.: Omega, 2007. - 400p.
23. Meskon M.Kh. Fundamentals of Management / M.Kh. Mescon, M.Albert, F.Hedouri. - M.: Delo, 1997. - 494 p.
24. Porshnev A.G. Organization management: Workshop / A.G. Porshneva - M .: INFRA-M, 2003. - 373 p.
25. Pugachev V.P. Personnel management of the organization / V.P. Pugachev. – M.: Aspect Press, 2005. – 279p.
26. Polovtseva F.P. Commercial activity: Textbook. - M .: Infra - M, 2005. - 248s.
27. Rapoport B.M. Optimization of management decisions. – M.: TEIS, 2006.-264p.
28. Remennikov V.B. Development of a management decision: Textbook for universities - M .: Unity - Dana, 2000. - 271s.
29. Saak A.E., Tyushnyakov V.N. Development of a management decision: Textbook / Saak A.E., Tyushnyakov V.N. - St. Petersburg: Peter, 2007. - 272p.
30. Sokolova L.E. Development of a management decision: Lecture notes. - M.: 2008. - 188s.
31. Smirnov E.A. Development of management decisions: A textbook for universities. - M .: Unity-dana, 2002. - 271s.
32. Snegireva V. Retail store. Assortment management by product categories. - St. Petersburg: Peter, 2007. - 416s.
33. Travin V.V., Dyatlov V.A. Enterprise personnel management / V.V. Travin, V.A. Dyatlov - M .: Delo, 2002. - 297 p.
34. Teacher Yu.G. Development of management decisions: Textbook / Yu.g. Teacher, A.I. Ternova, K.I. Ternovoy - 2nd ed., Rev. and additional - M .: Unity - Dana, 2007. - 383 p.
35. Chuikin A.M. Development of management decisions: Textbook. – Kaliningrad University. - Kaliningrad, 2000. - 150s.
36. Fatkhudinov R.A. Management decisions: Textbook. - M .: Infra - M, 2007. - 344 p.
37. Tsypkin Yu.A., Lyukshinov A.N., Personnel management / Yu.A. Tsypkin, A.N. Lyukshinov - M.; Mir, 2004. - 406s.
38. Tsygichko V.N. decision-making leader. M.: INFRA-M, 2004. - 178s.
39. Eddous M., Stensfield R. Methods of decision making / Translated from English, Ed. I.I. Eliseeva. - M .: Banks and stock exchanges, 2004. - 590s.
40. Evans, James R. Quality Management - M .: Unity - Dana, 2007.- 671s - (Series "Foreign textbook)
Annex 1
Organizational structure of ZAO Vneshtorgsib-M
1. Classification of management decisions
To characterize the presented classifications of management decisions:
On the basis of acceptance: intuitive, based on judgment, rational;
According to the degree of impact on the object: operational, tactical and strategic;
In order of adoption: individual, collective and collegiate;
According to the criterion of novelty: routine, selective, adaptive and innovative;
According to the degree of regulation: directive, orienting and recommending;
By the style of decision-making - by the ratio of efforts at the stage of developing alternatives and their choice: inert, cautious, balanced, risky, impulsive.
Present and characterize three more approaches to the classification of management decisions (10 classifications in total).
Give examples of each listed classification of management decisions.
The classification of managerial decisions according to the degree of impact on the object is shown in fig. 1.1.
Rice. 1.1 - Classification of management decisions on the basis of adoption
Intuitive Solutionsis a choice made only on the basis of the feeling that it is correct. In a complex organizational situation, thousands of choices are possible. For a leader who relies solely on intuition, statistically speaking, the chances of right choice without any logic application are low.
Example:
When making a purely intuitive decision, people are based on their own feeling that their choice is correct. Here there is a "sixth sense", a kind of insight, visited, as a rule, by representatives of the highest echelon of power. Middle managers rely more on the information they receive and the help of computers. Despite the fact that intuition sharpens along with the acquisition of experience, the continuation of which is precisely a high position, a manager who focuses only on it becomes a hostage to chance, and from a statistical point of view, his chances of making the right choice are not very high.
Judgment Based Decisionsis a choice based on knowledge or experience. A person uses knowledge of what has happened in similar situations before to predict the outcome of alternative choices in the current situation. However, we note that a leader who is overly committed to judgment and accumulated experience may consciously and unconsciously avoid interacting with new technologies and developments, which leads to irrational decisions.
Example:
The decision to give the competent secretary the right to answer all routine correspondence without external control. The manager's decision on where to build a warehouse for finished products.
Rational Decisionis a decision that is based on an analytical process and is often independent of prior experience.
Stages of acceptance rational decision: problem diagnosis, formulation of constraints and criteria for decision-making, identification of alternatives, analysis and evaluation of alternatives, final choice of an alternative, implementation of a solution, feedback, evaluation of results.
Example:
Choosing (purchasing) a car. The choice of the sales market for goods based on the marketing research.
The classification of managerial decisions according to the degree of impact on the object is shown in fig. 1.2.
Rice. 1.2 - Classification of management decisions according to the degree of impact on the object
Strategic Management Decisions- these are decisions that are made at the highest level of management for the long-term development of the organization. These solutions are followed by the development of: strategic plan, production program of the organization. Strategic decisions involve fundamental restructuring of the organization: changing directions financial flows into product groups or target segments, transformation of the structure, entry into new regional markets, expansion or reduction of activities, change assortment policy. Strategic management decisions are made at the level of directors, vice presidents of the company, deputy. directors, heads of production departments and workshops. In a small business, the entire responsibility for making strategic decisions concentrated in the hands of the leader and his team.
Strategic - these are directive acts that direct, organize and motivate the collective actions of people to achieve strategic goals. Strategic planning includes:
policy development in various areas that determine the life of the organization;
development of programs and projects, forecasting and determination of socio-economic development.
Strategic management decisions are designed to ensure that the organization fulfills its mission and, due to this, its survival in a highly competitive environment.
Example:
The car manufacturing plant decides whether to produce any spare parts for the cars themselves or find a supplier to purchase them from.
Operational management decisionsperform a corrective role directly in the course of the production activities of the enterprise, solving problems that suddenly arise and cannot be delayed.
Operational management decisions are made on a daily basis based on the conditions of production activities, resource provision, market demand, prices, social demands, events in the political, economic, social, environmental environment. Feature: operational decisions are sensitive to the emerging unforeseen situation, in this regard, they are called situational.
The subject of operational decisions: organizational measures, urgent orders, replenishment of emerging losses, losses, replenishment of missing material, labor, financial resources, adjustment of planned, program activities, obtaining current benefits.
Programmed decisions have the greatest weight in the totality of operational management decisions, since operational decisions are fleeting, urgent in nature, require the fastest possible execution and immediate response to the situation.
Example:
Repairing a broken machine in the workshop. Fixing a computer in the office. Software installation.
Tactical Management Decisions, as a rule, are focused on the short and medium term and problems of an industrial and technical nature.
Tactical management decisions are associated with medium-term problems, the development of a line of action for a relatively short period of time in accordance with the current situation in production and markets. Tactical decisions are a way of concretizing the strategy, translating it into specific measures to be implemented within a certain planning, program period.
Orientation of tactical management decisions: as a rule, such decisions are aimed at achieving intermediate goals, solving problems that contribute to the promotion and general goals.
Example:
Decisions of the company (manager) on the conditions under which the enterprise will agree on supplies necessary equipment(software).
Operational and tactical decisions are related to the implementation of current goals and objectives. In terms of time, they are calculated for a period not exceeding a month.
The classification of managerial decisions according to the order of adoption is shown in fig. 1.3.
Rice. 1.3 - Classification of management decisions in order of adoption
Collegial decisionis a decision made by a group of managers and specialists.
As a rule, decisions are made by the head of the organization in agreement with the leading top managers and specialists, collectively. This is what happens in most companies. The head delegates parallel powers or uses the method of mandatory approval, which is written in the administrative documents: as “agreed”. With mandatory approvals, the responsibility for making significant decisions is partially assigned to the managers who assume such powers. Parallel powers increase the responsibility and rights of managers, and the decision becomes collective. For example, many companies use parallel powers to control financial expenses, and in the case of large purchases, two or three executive signatures are required.
Collegiate decisions are usually made at business meetings and during the work of commissions by leading managers and specialists. At such meetings, there is already a known balance of power, which significantly affects the result of management, the decision.
Example:
The head attracted an external law firm for advice on any legal issues.
Collective (democratic) decisions- these are decisions made by the majority of the employees of the organization, jointly by the labor collective or a small group. Unlike collegial decisions, democratic decisions are a vivid expression of the will of the majority of members of the labor collective, small or large. Such decisions are made by secret ballot, using methods expert assessments, for example, nominal group technique, Japanese "ringi" techniques. The use of such methods is possible with a high level of staff motivation, the use of a democratic leadership style, the development and transparency of the corporate culture.
Collective decisions are also made when significant problems and issues affecting all personnel are raised.
Example:
Election of the head of the competition, implementation new system wages, etc.
Individual management solutionsThese are decisions that are made by the leader alone. In small business organizations, a small number of management levels, a high degree of risk of losing competitive status. Such an organization is led by an entrepreneur who bears full responsibility for its further functioning in unstable market conditions. The entrepreneur is afraid to delegate authority on financial and other significant issues to his subordinates and makes decisions on his own. The positive aspect of an individual solution is its creative, extraordinary character.
The shortcomings of individual decisions become apparent when they acquire an authoritarian character. The head usurps power, single-handedly manages resources, determines the personnel policy of the organization and puts pressure on subordinates. Decisions made by the leader alone allow the organization to remain in the market for some time and be successful. However, in the future, the leadership style used by the leader slows down the development of the organization. The leader must be able to maneuver and be flexible, use the art of delegating decision-making authority to other people in the organization.
Example:
The manager decided to prepare presentation material for the meeting on his own, without resorting to the help or cooperation of employees (employees).
The classification of managerial decisions according to the criterion of novelty is shown in fig. 1.4.
Rice. 1.4 - Classification of management decisions according to the criterion of novelty
routine decisionsare accepted in accordance with the existing program, the manager must identify the situation and take responsibility for initiating certain actions. Difficulties here can arise if the manager is incompetent, misinterprets the available instructions for a particular situation, acts illogically or shows indecision. A leader who perceives the situation correctly, draws the right conclusions, acts reasonably and controls the consequences, achieves what is expected of him. At this level, no creativity is required, as all procedures are predetermined.
Example:
Where to put the computer on the desktop.
At selective decisionsa certain amount of initiative and freedom of action is required, but within certain limits. Selective decisions suggest that the leader evaluates the merits of a whole range of possible solutions and tries to choose those actions that are best suited to a given problem, are the most effective, economical.
Effectiveness depends on the manager's ability to choose the most likely course of action and whether it will be acceptable, economical and effective.
Example:
The choice (rather than the development of a new one) of the system of motivation and incentives for personnel.
Adaptive Solutionscause difficulties, since here the leader is looking for a new solution to a known problem, he must be able to abandon the usual, but already outdated approach to the problem and develop a creative solution. The leader's success depends on his personal initiative and ability to make a breakthrough into the unknown. Such decisions provide an answer that could have existed before, but in a different form. The leader is looking for a new solution to a known problem.
Example:
Innovative Solutionsthe most complex, the manager needs to find ways to understand completely unexpected problems, and solving such problems requires new ideas and methods, the ability to think in new ways, the ability to creatively solve the problem by discussing and using the creative ideas of other specialists.
The leader must be able to understand completely unexpected problems, the solution of which requires the manager to develop in himself thinking in relation to changing conditions. It is possible that in order to solve today's complex problems, it may be necessary to create a new branch of science or technology.
Development of a new (innovative) approach to organizing and conducting conference calls, for example, via IP-telephony or Skype (Skype).
Classification of management decisions according to the content in fig. 1.5.
Rice. 1.5 - Classification of management decisions by content
Decisions that have quantitative characteristics, are taken on the basis of mathematical and statistical methods. The assessment of quality and efficiency in this case is simplified, since the achieved level is compared with the planned one.
Example:
Decreased defectiveness of finished products by 5%.
Decisions that do not have quantitative characteristics, are subjective in nature, since they are determined by the personality of the subject who receives them. The assessment of their quality is complex and rather controversial, since it is also subjective.
Example:
Carrying out the procedure of rotation (rearrangement) of personnel of the enterprise
The classification of managerial decisions according to the degree of regulation is shown in fig. 1.6.
Rice. 1.6 - Classification of management decisions according to the degree of regulation
Directive decisionsmust be fulfilled and do not imply any initiative. They establish a clear relationship between certain parameters and specific solutions.
Example:
Making a decision on the introduction of information and communication technologies in the field municipal government will guide those responsible for its implementation.
Orienting decisionsdetermine the possible options for the activities of employees when certain conditions occur.
Example:
The decision will be orienting for archive workers, as it informs them that soon the work of many of them will not be in demand. At the same time, it provides for the training of specialists to work with the municipal information system.
Example:
The same decision for different categories of performers can be directive, orienting and recommending.
The classification of managerial decisions according to the style of decision-making is shown in fig. 1.7.
Rice. 1.7 - Classification of management decisions by decision-making style
The nature of the development and implementation of managerial decisions strongly depends on the personal characteristics of a person.
Balanced Decisionsare accepted by managers who are attentive and critical of their actions, put forward hypotheses and their testing. Usually, before starting to make a decision, they have formulated the initial idea.
Example:
Despite the complaints of some members of the team against their immediate supervisor, the director does not apply sanctions to him, since the complaints turned out to be rumors spread on purpose.
impulsive decisionsare accepted by leaders who easily generate a wide variety of ideas in unlimited quantities, but are not able to properly test, refine and evaluate them. Decisions therefore turn out to be insufficiently substantiated and reliable;
Example:
The dismissal of a leader against whom there are unverified complaints from his subordinates.
Inert solutions- the result of a careful search. They are dominated by control and clarifying actions over the generation of ideas, so it is difficult to detect originality, brilliance, and innovation in such decisions. They weakly activate the staff for their implementation.
Example:
Conducting an internal audit
risky decisionsare taken without careful justification of actions by a leader who is confident in his abilities. Typically, such leaders have good rears in the form of constantly supporting their superiors or subordinates. They may not be afraid of any danger.
Example:
Cautious Decisionsare characterized by the thoroughness of the manager's assessment of all options, a supercritical approach to business, and a large number of approvals. Such managerial decisions are effective in solving problems related to human life and its environment.
Example:
The decision to increase the travel expenses of the company's lawyer after all possible complex analysis his presence and absence at preliminary hearings on various lawsuits and the consequences of these trips.
The classification of management decisions according to the content of the management process is shown in fig. 1.8.
Rice. 1.8 - Classification of management decisions according to the content of the management process
Economic Solutions connected with the economic system, necessary for growth economic efficiency activities of the organization, profitability, payback and liquidity of assets. How best to manage resources, make the enterprise profitable, increase profits - these and other questions will face the manager who makes economic decisions.
Economic management decisions are manifested in the fact that the development and implementation of any management decision requires financial, material and other costs. Therefore, every management decision has a real value.
The implementation of an effective management decision should bring direct or indirect income to the company, and an erroneous decision or a decision misunderstood by subordinates leads to losses, and sometimes to the termination of the company.
Example:
If the manager decides to fire a negligent employee, then the latter may suffer greatly, and if you do not fire or take other measures of influence, the entire organization may suffer.
Social Solutions- these are decisions affecting the social structure of the organization, personnel, corporate culture, climate and shared values. Social decisions can be related to the optimization of the work of personnel, improvement of the system of motivation and social support for employees, the image of the organization in society, and the implementation of the mission.
Example:
Raising wages, introducing environmentally friendly equipment, improving sanitary conditions, strengthening safety requirements, resolving conflicts.
Organizational decisions- these are decisions related to management methods, ways to achieve goals. Such decisions are an integral part of the management process.
The essence lies in the fact that the personnel of the company is involved in this work. For effective work, it is necessary to form a workable team, develop instructions and regulations, give employees powers, rights, duties and responsibilities, establish a control system, allocate the necessary resources, including information, provide employees with the necessary equipment and technology, constantly coordinate their work.
Example:
Organize employees to complete the task, redistribute functions and powers, conduct general meeting.
Technical solutions - these are operational decisions that are necessary to ensure labor, production processes, supply with the necessary resources, materials, information.
Example:
Install software in a department, replace a broken machine, pay travel expenses, send a worker to an important production site.
The classification of management decisions according to the method of fixing the management process is shown in fig. 1.9.
Rice. 1.9 - Classification of management decisions according to the method of fixing the management process
Management decisions can be expressed in terms of writingas administrative documents in the form of orders and instructions. Managers provide written decisions for legal examination and further for execution.
Example:
Application for hiring a new employee
In emergencies, the oral form is used. The disadvantage of this method is that the performers sometimes distort the content, and not always consciously, and interpret the solution in their own way.
Verbal management decisionsalso have legal force, and they can be challenged in court if there are at least two people who have heard these decisions.
Oral management decisions occur in the process of meetings, meetings and business conversations. Gatherings and meetings are collective events (public or with the involvement of a wide range of participants); conversations are conducted mostly individually or with a small number of people gathered.
Example:
Oral order to establish the working hours on the day off
Electronic Solutionsinvolves fixing decisions on electronic media. This method allows you to use all the possibilities of information and communication technologies. After the adoption of the Federal Law No. 149-FZ of July 27, 2006 "On Information, Information Technologies and Information Protection", the electronic method of fixing decisions has become widespread.
Example:
Giving by a leader to a subordinate through Email documentation for negotiations
In the practice of enterprises from the position legal registration management decisions the most common are written management decisions.
The classification of managerial decisions according to the method of information processing is shown in fig. 1.10.
Rice. 1.9 - Classification of management decisions according to the method of information processing
Algorithmic solutionsinvolve a strict formalization of the execution of procedures and operations based on rules, algorithms, formulas, statistical data.
Example:
The calculation of the economic efficiency of new production should be carried out according to the developed algorithms.
But in management, not everything can be quantified. Something is valued qualitatively. You can process and evaluate information based on intuition, generalizations, ideas, experience, associations. Through conversation, discussion, asking leading questions, you can get new information from the client, partner. Such solutions are called heuristic.
Example:
Obtaining information from the partner about discounts received for office paper from the same supplier stationery.
2. Target and processor technologies
managerial business processor
Target Technologies
Provide examples of the application of each of the target technologies both in business and in the field of educational and extracurricular activities at the university. Provide at least two examples for each area.
Processor technologies
Provide at least two examples of each of the processor technologies.
Target Technologies
Target technologies are technologies based on the priority of goals over situations. Target technologies orient decisions towards achieving the goal, rather than eliminating disturbing influences.
The classification of target technologies is shown in fig. 2.1.
Regulatory technologyconsists in issuing tasks (goals, tasks) for the execution, indicating the means and their possible limitations, recommended methods and the approximate time for their implementation. The technology provides for a strict control of the process of approaching the target.
The professionalism of the assignment is determined by the qualifications of the manager who issued the assignment and the performer. It implies strict control over the positive dynamics of the process of completing the task.
Regulatory technology can lead to two main outcomes:
achieving tangible positive results from the very process of achieving the goal;
the absence of significant positive results within an acceptable time (marking time).
Regulatory technology provides for the development by the head of the ultimate goal of management and strategies with the possible limitation of various resources (material, human, financial, etc.). In this case, the goal will certainly be achieved, but within a timeframe that is difficult to determine in advance. Achieving the goal is guaranteed only with strict internal or external control over the progress of the process of implementing the goals.
the time to complete the goal or its constituent tasks should not be precisely set (the process of achieving the goal itself is important);
a significant and unpredictable limitation of resources (financial, technological, raw materials, etc.) is possible;
innovative and long-term nature of developments;
Estimated time to achieve the goal - more than 1 year.
This technology is based on statistical methods, the theory of fuzzy sets, the theory of developing solutions under uncertainty. The authorship of the program and the results obtained belongs to the leader and the performer.
Example:
Book writing. Preparation and writing student work(thesis project, term paper, etc.).
Drawing up a business plan.
Initiative-targeted technologyis based on the issuance of tasks without specifying the means and methods for their implementation and is designed for an enterprising and professional performer.
The initiative-target technology provides for the development by the manager of only the final goal of the task for the employee or department, as well as the deadline without specifying the mechanism for achieving it. At the same time, the goal may not be achieved for any reason, it may be achieved on time or earlier, or it may be achieved outside the established period.
Initiative-target technology gives a lot of room for initiative decisions of subordinates.
Basic conditions for using this technology:
the staff of the organization or its subdivision is not more than 10 people;
the time for completing the assignment should not exceed one month from the date of its issuance;
high professionalism of the staff or great confidence in him on the part of the head;
production of new goods, services, information or knowledge;
the presence of stable informal relationships in the team.
The professionalism of the assignment is determined by the qualifications of the performer of the assignment, and the qualifications of the leader plays a secondary role. Technology does not guarantee the achievement of the goal.
Example:
In the process of completing the task assigned by the manager to the employee, the specialist quit, resulting in a significant decrease in the required resources.
To reduce occupational diseases, the company's management decided to purchase a technology that does not use asbestos as fillers for building blocks, while the construction of a new technological building was decided to be “frozen”.
Program-targeted technologymost commonly used in organizations. It consists in the issuance of tasks (goals, tasks) for the execution, indicating the means, methods and time for their implementation, there are indications of external or internal control intermediate states of this execution.
The professionalism of the assignment is determined by the qualifications of the leader who issued the assignment, and the qualifications of the performer plays a secondary role. Program-target technology usually guarantees the achievement of the goal.
The application of program-targeted technology can lead to three main results:
achievement of the goal within the specified period with acceptable deviations from the specified intermediate values;
achievement of the goal within the specified period with significant deviations from the specified intermediate values;
sustainable failure to achieve the goal in a given time frame.
This technology provides for the development by the manager of management goals, means and methods for their implementation, as well as the timing and states of intermediate values of the process. If any specified intermediate value is not achieved, then additional resources are allocated for its implementation, if the specified intermediate value exceeds the planned one, then part of the resources is transferred to other needs and the goal will be achieved within the stipulated time.
Program-targeted technology is based on modern knowledge, economic and mathematical methods and information technologies.
The main conditions for the use of this technology:
certainty and availability of management and production resources;
a pronounced separation of management and production;
a large volume of standard procedures, situations and decisions.
Example:
When developing a political platform for any political organization in which its leader is the ideologist and conductor of a set of measures. In this case, the qualification of the performer plays a secondary role, and the professionalism of the task is determined by the qualifications of the leader who issued the task.
Development and implementation, for example, of the Federal Target Program "State Border Russian Federation»
Processor technologies
For successful implementation, each target technology for the development of management decisions has its own set of processor technologies, representing the mechanism for implementing the target technologies.
The processor includes six control technologies (see Figure 2.2).
Rice. 2.1 - Classification of target technologies
Results Based Technologyis based on the priority of final results over planning and forecasting. The main function implemented by managers is the coordination (adjustment) of actions and decisions depending on the result obtained.
This technology is well implemented for medium and small organizations or departments in which:
the time between decision-making and the result of their implementation is minimal (hours, several days);
there are no insurmountable difficulties in the rapid acquisition of the required resources or the return of unclaimed ones;
the professionalism of the head of the organization or the project manager is high enough;
the nature of production is predominantly mechanized.
The basis of this technology is a business plan and developments for making managerial decisions in the face of possible uncertainties. It is known that the most necessary factors for the development of an effective management decision are either unknown or cannot be precisely determined.
This technology is the cheapest among other technologies, since it does not require the development of detailed plans and the calculation of funds for the implementation of solutions.
Example:
1. solving and writing independent work on the exam.
Planning a report on the annual volume of sales of products (services).
Management technology based on needs and interestsis based on the priority of interpersonal relations over other means and methods for the formation of interaction between employees involved in the implementation of the goal.
Interaction between a leader and a subordinate in the implementation of this technology can only occur if the impact affects the needs and interests of both the leader and the subordinate. All other variants of influences lead to counteraction of the subordinate.
This technology is effectively implemented in large and medium-sized organizations in small regions (cities, towns, etc.), where the organization's activities significantly affect the municipal infrastructure.
The number of personnel involved in this technology is not limited. The main function implemented by managers is the planning and organization of interaction between participants labor process, a positive result is guaranteed.
Example:
Creation of an enterprise in cities and towns with a developed textile industry, where one large organization gives life to a number of smaller service enterprises.
Opening of a new city library in a place where public transport
Management technology through constant checks and indicationsis based on the priority of control and strict personnel management over other means and methods for the formation of interaction between employees involved in the implementation of the goal. Control and strict management are justified by the fact that in this case a person better realizes his needs for self-expression, self-manifestation, stability and order.
This technology is effectively implemented in small organizations in which the authority and professionalism of the leader is beyond doubt, especially in new knowledge-intensive organizations, educational institutions or in enterprises where management consultants work on a contract basis.
Example:
1. Testing, attestation, examination, knowledge testing by the teacher of students.
Choreography for the play. In this case, the leader of the group (choreographer) is the authority that regulates and controls every movement of the dancer (actor).
Control technology in exceptional casesbased on the priority of the professionalism of the performers or a proven and well-performed production technology over other means and methods for the successful completion of assigned or selected tasks.
This technology is effectively implemented in small organizations operating either on a strictly regulated technology, or in organizations with a trust (functional) management structure.
In this structure, the manager exercises a linear influence on all areas of the production process according to administrative functions, and in economic, technological and other functions provides subordinates and colleagues with the required assistance. The leader is in a situation: equal among equals. The contractor can also transfer part of his work to a lower level and act in relation to him as a line manager and as an adviser.
Example:
1. Fulfillment by the accountant of the order of the chief accountant for the preparation and submission of reports to the director of the enterprise.
Instructing the teacher to the student to public lesson.
Control technology based on " artificial intelligence» is based on the priority of proven practice, statistics and modern economic and mathematical methods implemented in the form of knowledge bases or databases using modern information computer technologies.
This technology is especially effective for any organization with a large volume of typical complex procedures.
Example:
Filtering e-mail using a computer. In this case, the most important letters are first submitted to the head of the enterprise for consideration.
Maintaining journals of student progress in universities.
Management technology based on personnel activationis based on the priority of incentives and rewards for the employee over other means and methods for the successful completion of assigned or selected tasks. It is effective in predominantly manual production, when labor productivity and product quality are mainly determined by the mood, psychology and health of the worker, as well as the socio-psychological climate in the team. The number of employees is unlimited. The technology requires a monitoring system for the effect of incentives and rewards on the activities of each employee or team.
This technology affects the satisfaction of the needs and interests of employees not directly from the manager, as in the management technology based on needs and interests, but through the decisions of the employee himself. Technology requires a high level vocational training personnel specialists.
Example:
Stimulating an employee by issuing him a responsible task or paying remuneration in cash and (or) commodity forms.
Writing essays, self-study of educational literature as a student's motivation to receive automatic final grades for the semester (year).
List of used literature
1.Abryutina M.S., Grachev A.V. Analysis of the financial and economic activity of the enterprise. - M.: Publishing house "Business and Service", 2010. - 256 p.
2.Baldin K.V., Vorobyov S.N., Utkin V.B. Management decisions: Textbook. - M.: Dashkov i K, 2007. - 496 p.
.Batrik R. Technique for making effective management decisions: Textbook. - 2nd ed. - St. Petersburg: Peter, 2010. - 416 p.
.Vertakova Yu.V., Koz'eva I.A., Kuzbozhev E.N. Management decisions: Textbook. - M.: KnoRus, 2009. - 352 p.
.Vertakova Yu.V. Management decisions: development and choice: Textbook. - M.: KNORUS, 2010. - 422 p.
.Garkusha N.M. Models and methods of decision making in analysis and audit: Textbook / Ed. N.M. Garkushi, O.V. Tsukanova, O.O. Goroshskaya. - 2nd ed. - K.: Knowledge, 2012. - 591 p.
.Golubkov E.P. Management decision-making technology: Textbook. - M.: Delo, 2010. - 544 p.
.Zlobina N.V. Management decisions: Textbook. - Tambov: TSTU, 2007. - 80 p.
.Kokoreva T.A. System analysis of decision-making procedures. - M.: Timber industry, 2009. - 290 p.
.Litvak B.G. Development of a management decision: Proc. - 3rd ed. - M.: Delo, 2011. - 288 p.
.Litvak B.G. Development of a management solution. - 4th ed., Rev. - M.: Delo, 2012. - 392 p.
.Mashchenko V.E. System corporate management: Textbook. - M.: Sirin, 2013. - 251 p.
.Raizberg B.A., Lozovsky L.Sh., Starodubtseva E.B. Modern economic dictionary. - 5th ed., revised. and additional - M.: INFRA-M, 2007. - 495 p.
.Smirnov E.A. Development of management decisions: Textbook. - 2nd ed., add. - M.: 2012. - 271 p.
.Smorchkov A.V. Development of management decisions: Textbook. - Part 2. - Bryansk: BSTU, 2011. - 44 p.
.Travin V. Preparation and implementation of management decisions: Textbook. - M.: Delo, 2008. - 80 p.
.Fatkhutdinov R.A. Management decisions: Textbook. - 5th ed. - M.: INFRA-M, 2008. - 314 p.
.Shemetov P.V., Radionov V.V., Cherednikova L.E., Petukhova S.V. Management decisions: Textbook. - 2nd ed., add. and dorab. - M.: Omega-L, 2012. - 400 p.
Tutoring
Need help learning a topic?
Our experts will advise or provide tutoring services on topics of interest to you.
Submit an application indicating the topic right now to find out about the possibility of obtaining a consultation.
Test
On discipline "Management"
On the topic of: Methods of making managerial decisions on the example of an enterprise Company "Industrial materials"
Introduction…………………………………………………………………………….3
1. Methods of making managerial decisions……………………….……...…4
2. Identification of problems in the activities of CJSC Prommaterialy………………7
3. Decision making on the example of the activities of Prommaterial CJSC……..13
Conclusion………………………………………………………………………….18
List of used sources…………………………………………...20
Introduction
Creation of a large number of enterprises various forms ownership during the formation of a market economy in our country led to the fact that managers had to learn to manage on their own, and not at the behest of "above". One of the elements of independent management of the enterprise is the adoption of managerial decisions.
The process of making managerial decisions is relevant due to the fact that the scale, number of elements and relationships of subsystems in organizational systems are expanding more and more.
Management decisions can be made in relation to any area of the organization: personnel management, financial management, production process management, including marketing service management.
The purpose of writing this work is to eliminate the unsatisfactory work of the enterprise through the development and adoption of a management decision in the field of the marketing component of the company's activities.
The object of the study is the company CJSC Prommaterial.
The relevance of the work is explained by the fact that the existence of any organization is impossible without the constant daily adoption and implementation of certain decisions at various levels of management. At the same time, managerial decisions are aimed at achieving the most optimal result of the activity of the organizational and production system.
The object of management is the marketing structure of the analyzed enterprise. The subject of management is the management system of Prommaterial CJSC.
The result of making a rational management decision is to increase the performance indicators of CJSC Prommaterial.
1. Methods for making managerial decisions.
A management decision is a fixed management act expressed in writing or orally and implemented to solve a problem situation.
Making a managerial decision is the process of choosing a reasonable alternative to solving a problem, which is a key moment in the management system. The results of the implementation of the adopted management decisions serve as the most objective assessment of the art of the leader.
Management decision-making methods are specific ways in which a problem can be solved.
Management decision-making methods:
Presentation of complex problems as a set of simple questions.
2. Diagnostics.
Search in the problem most important details which are dealt with first. Used with limited resources.
3. Expert assessments.
Any ideas are formed, considered, evaluated, compared.
4. Delphi method.
Experts who do not know each other are asked questions related to solving the problem, the opinion of a minority of experts is brought to the opinion of the majority. The majority must either agree with this decision or refute it. If the majority disagrees, then their arguments are passed to the minority and analyzed there. This process is repeated until all experts come to the same opinion, or go to the fact that groups stand out that do not change their minds. This method is used to achieve efficiency.
5. Non-specialist method.
The question is solved by persons who have never dealt with this problem, but are specialists in related fields.
6. Linear programming.
7. Simulation modeling.
8. Method of probability theory.
9. Method of game theory.
Problems are solved in conditions of complete uncertainty.
10. Method of analogies.
Search for possible solutions to problems based on borrowing from other management objects.
In order to be effective, i.e. to achieve certain goals, the solution must satisfy a number of requirements:
1) be real, i.e. proceed from achievable goals, actually available resources and time (therefore, the solution should contain goals, decomposition (partition) of goals into tasks, assessment of available and required resources, a scenario for achieving goals as a result of solving problems and other elements of an appropriate focus);
3) be stable in terms of efficiency to possible errors in the determination of the initial data (robust);
4) prepare, accept and execute in real time those processes that are controlled, taking into account the possible rates of development of contingencies, emergencies(sometimes they try to ignore this most important requirement. Only control in regular situations is considered);
5) be realizable, that is, do not contain provisions that will disrupt execution as a result of the conflicts it generates (For example, the discrepancy between the functions of departments and the technologies used generates a linear-functional conflict in the organizational and production system (OPS0);
6) be flexible, that is, change the goal and (or) the algorithm for achieving the goal when external or internal conditions change, contain a description of the states of the control object, the external environment, in which the implementation of the solution should be suspended and the development of a new solution should be started;
7) provide for the possibility of verification and control of execution.
Goals and objectives must be realistic, correlated with the available resources and their types for solving specific problems, as well as the methods and technologies that are supposed to be used. This involves the use of various types of normalization in forecasting and planning decisions.
2. Identification of problems in the activities of CJSC"Industrial materials".
The enterprise CJSC Prommaterialy considered in the work is engaged in the production and sale of building materials. The company was founded on the basis of a former supply base six years ago. This explains the fact that the company has a staff of production specialists, and the sale of products is ill.
You can imagine the enterprise under consideration as a system. The following is a table of functions and elements of the organization.
To diagnose problems and further forecasting, it is necessary to conduct a detailed analysis of the object of forecasting.
The purpose of the analysis is to obtain the information necessary to diagnose the problem and predict the development of the control object in the interests of making a decision by the manager.
The analysis involves the study of:
macro environments;
Competitive environment;
internal environment.
In the influence of tastes and preferences of consumers on the range of products;
In the actions of competitors;
In the regulation of the organization's activities by state and other authorities, etc.
The political processes taking place in the country also have an indirect impact to the extent that the purchasing power of the population decreases in relation to all goods and services, and in particular to building materials.
The analysis of objects and subjects of management is carried out in a systemic unity with the analysis of the external environment.
The analysis involves the study of the macro environment, the competitive environment, the internal environment.
Like any system, the organization under consideration operates in the aggregate and in interaction with the external environment. This interaction is manifested in the following:
In the procurement of raw materials and materials from third-party suppliers;
In the selection and change of personnel;
Influencing the tastes and preferences of consumers on the assortment
manufactured products;
In the actions of competitors;
In regulating the activities of the organization by
state and other authorities, etc.
Analysis of the macro environment showed that the company is influenced by the legal authorities in the field of compulsory licensing of activities and certification of products. This influence is felt in daily activities, but does not carry a negative impact and reduce the effectiveness of activities. The costs incurred by the enterprise in the course of the implementation of the listed activities are attributed to the decrease in profits.
The development of scientific and technological progress and the achievements of modern technologies have a greater influence compared to the previous parameters. This is reflected in the development modern materials and technologies for their production, as well as in the improvement of traditional construction methods. This process reduces the competitiveness of traditional building materials and technologies and forces them out of the market.
The analysis of objects and subjects of management is carried out in a systemic unity with the analysis of the external environment. The study of the competitive environment made it possible to reveal the fact that direct competitors, i.e. manufacturers of similar products do not have a strong impact on consumers, market segments are divided approximately proportionally. There is its own circle of regular consumers in the form of large industrial enterprises and construction organizations. Manufacturers of a morally different range of building materials have taken away some of the consumers and have little impact on the emerging market conditions.
The block diagram of monitoring and diagnosing the problem is shown in Figure 1.
A problem has been detected in the enterprise. A problem is a critical discrepancy between the desired and actual state.
In this case, this is well-established production and poorly organized sales, while with good production, sales should not lag behind in order to be able to invest free financial resources in an even greater expansion of production or its improvement.
Awareness of the problem consists in establishing the fact of its existence based on the results of monitoring activities or researching market opportunities. The problem, which has reached a certain severity, is transformed into a motive for the activities of the organization and its managers.
3. Decision making on the example of activity CJSC "Prommaterial"
According to the materials presented on the work done to identify problems, the most important for strategic development enterprise problem. It is connected with the restructuring of the principles of work of the marketing division of the company. Within the framework of solving this problem, several directions of its solution can be distinguished. On the one hand, this is a change in the methodological approach to the organization of the marketing service at the enterprise. And on the other hand, this is a change in the influence of the human factor on solving the problem.
You can offer several options for solving this problem, given below in the form of a decision tree (Figure 3):
The algorithm for choosing a method for solving a specific problem is shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4. Algorithm for choosing and making a managerial decision.
Form a new structure of the marketing department of the company.
1. Accept as the main one in the system of motivation of personnel activity
a program of material interest of personnel in increasing sales volumes and bonuses based on the results of the company's activities for each quarter.
2. Build a sales system through the involvement of dealers and distributors
on a contractual basis.
3. Set the pricing policy according to the "cost plus" system.
4. Conduct a market research of building materials and
consumer preferences, and then develop a range of products and production program according to research results.
Of the proposed ways to solve the problem, two satisfied the company immediately:
first, change pricing policy is not possible, because this market independently regulates the price level based on supply and demand;
secondly, changing the structure of the marketing service is not considered appropriate, because the company has qualified specialists, and the search for new personnel will take time and lead to additional costs Money.
Only options for changing the sales strategy based on a study of customer demand remained realistically possible.
To make a decision that requires the identification and consideration of a significant number of factors, it is advisable to involve those employees who are more or less familiar with the problem posed and will be able to give certain recommendations when considering it. It is noted that group decisions are effective provided that the group is small in composition and the number of its members has the possibility of direct communication to discuss decisions. At the same time, the value of a decision made by a group is higher and its competence is greater than that of a decision made alone.
So, a decision was made to change the sales strategy while simultaneously studying consumers and their demand for products.
To do this, the following goal tree was compiled (see Figure 5).
Figure 5. Goal tree.
In accordance with the above decision tree, it is necessary to establish all risk points in order to exclude them in advance from practical activities firms. For the considered manufacturing enterprise"Prommaterial" the following risk situations can be distinguished:
Developed range of products, not in demand on the market and
there was a need for an urgent sale of commodity balances in order to prevent the stoppage of the production process;
A technological failure has occurred, which resulted in non-execution
contractual obligations and additional costs for the restoration of the production process and penalties;
There was a break in the contractual relationship with one of the dealers,
which bore the main load on the sale of products, which can cause stagnation of finished products in the warehouse;
To localize the above risk situations, one can cite a variant of possible activities with several dealers at once and the simultaneous maintenance of one's own distribution network. This means that it is necessary to enter into agency agreements with several firms simultaneously in order to prevent a failure in activities due to failures in the work of one large agent. At the same time, the issue of coordinating delivery and shipment schedules is acute in order to avoid non-cyclicality in the implementation process. That is, the schedule should be drawn up in such a way that in each period of time the products must be received by any dealer, and if there is a need to accumulate a large volume of products for one consumer, then products are not shipped to other consumers at this time.
On the other hand, it is necessary to produce several types of products, and not rely on any one product, so that there is interchangeability.
Conclusion
The following is a list of the most important points of this examination:
1. The impulse of a managerial decision is the need to eliminate, reduce the relevance or solve a problem, i.e. approximation in the future of the real parameters of the object (phenomenon) to the desired, predictive ones.
2. To solve the problem, it is necessary to answer the following questions: what to do (object)? how to do (technology)? for whom (consumers)? at what price? with what parameters? at what cost? in what quantity? at what time? Where? to whom (performers)?
3. The main requirements for the quality of information for making a management decision: timeliness, reliability, reliability, complexity, targeting, legal correctness, multiple use, high speed collection and processing, the possibility of coding, relevance.
4. The main parameters of the quality of management decisions should include: the entropy index, the degree of investment risk, the probability of implementing the decision, the degree of adequacy of the theoretical model to the actual data.
5. The main conditions for ensuring high quality and efficiency of management decisions include: applying scientific approaches to the development of a solution, studying the influence of economic laws on the effectiveness of a solution, providing high-quality information, applying methods of functional cost analysis, forecasting, modeling and economic justification, building a tree of goals , ensuring the comparability of alternative options, multivariate solutions, legal validity, automation, motivation for a high-quality solution, the presence of a mechanism for implementing the solution.
6. Alternative options for management decisions should be brought into a comparable form in terms of time factors, quality of objects, scale of production, level of development, method of obtaining information, conditions for using the object, inflation factors, risk and uncertainty.
7. The principles of economic justification of management decisions include: accounting for the time factor, accounting for costs and results for life cycle object, application to the calculation of systematic and integrated approaches, multivariance, comparability of options, taking into account the factor of uncertainty and risk.
8. The company "Prommaterial" has identified a problem in its activities - the unsatisfactory construction of a system for marketing products with its successful production. This work, based on theoretical material, considers options for solving the identified problem.
As a result of the activities to develop a management solution for Prommaterial, a range of measures was developed to improve the sales system for products and the work of the marketing service, including activities for market research and the development of an appropriate product range, changes in the sales system through the creation of a dealer network.
In the process of developing a management decision, two more possible options were rejected - a change in pricing policy and a change in the personnel of the enterprise.
To make management decisions at the enterprise in question, methods such as decomposition, diagnostics, expert assessments and other methods of making management decisions listed in paragraph 1 were used.
List of used literature
1. American management on the threshold of the XXI century. J.K. Grayson Jr., C. O'Dale. - M, 2002.
2. Operations research and management. V.V. Trigubenko. - M. 1999
3. How to do business in Europe. W. Hoyer. - M. 1999
4. Career manager. L. Iacocca. - M, 2001
5. Management of the organization. / Ed. Z.P. Rumyantseva, N.A. Salomatina. - M, 2001.
6. Management. / Ed. F.M. Rusinova, M.L. Once. - M, 2002.
7. Management. O.S. Vikhansky, A.I. Naumov. - M, 2001.
8. Development of a management decision. Forecasting - planning.
Theory of Designing Experiments. V.V. Glushchenko, I.I. Glushchenko. - Zheleznodorozhny, 2004
9. Project management. / Ed. V.D. Shapiro. - St. Petersburg, 1999
Studying the activities of LLC "Element-Trade". Analysis of financial stability, business activity and profitability of the enterprise. Application of SWOT analysis to identify the strengths and weaknesses of the firm. Development of management decisions; evaluation of their effectiveness.
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Hosted at http://www.allbest.ru/
NOU VPO Humanities University
Faculty of Business and Management
Analysis of the process of making managerial decisions in the organization
(on the example of Element-Trade LLC)
6th year students, correspondence department
Bespamyatnykh Olga Vasilievna
Scientific adviser:
Dan. Mitsek E. B.
Yekaterinburg 2013
Introduction
Chapter 1. Theoretical foundations of the process of making managerial decisions in an organization
2.3 Analysis of the management decision-making process in Element-Trade LLC
2.4 Evaluation of the effectiveness of the management decision-making process at the enterprise
Chapter 3. Measures to improve the process of making managerial decisions in Element-Trade LLC
Conclusion
Literature
Application
Introduction
The relevance of the chosen research topic is due to the fact that the activity of each person is based on decision-making and it is always a choice among many alternatives. In the process of work, the manager is forced to make decisions on a daily basis. A managerial decision is distinguished by a special responsibility, because is of a public nature, affecting the interests of many groups of people, and therefore requires a particularly balanced scientific approach. Making a management decision is the choice of the best way to achieve any management goal in the process of analyzing options.
Management decisions are related to the performance of management functions, including planning, organization, coordination and control of any processes.
The purpose of this course work is to develop ways to improve the management decision-making system on the example of the activities of a limited liability company "Element-Trade". The set goal determines the formulation and consistent solution of the following tasks:
The study of the theoretical foundations of decision-making in management and methods for assessing the effectiveness of the decision-making process.
Study of the decision-making system in the limited liability company "Element-Trade" and evaluation of the effectiveness of the process of making managerial decisions at the enterprise.
Development of ways to improve the process of making managerial decisions in Element-Trade LLC.
In the process of developing measures to improve the decision-making process, it was proposed: changing the decision-making scheme, changing the document flow scheme.
The theoretical part examines the essence and significance of the decision-making process, the stages of the process of making managerial decisions in an organization, the methodology for assessing the effectiveness of the process of making managerial decisions. The analytical part provides a general description of the object of study (the dynamics of the main economic indicators are considered, a SWOT analysis of the process of making managerial decisions in Element-trade LLC was carried out). The design part presents methods for improving the process of making managerial decisions for each of the stages of this process.
When writing the work, scientific and educational publications on management, organization management and management decisions were used.
The initial basis for the analysis of the decision-making process in LLC "Element-Trade": statistics data, accounting data, orders, regulatory documentation.
The object of the study is commercial enterprise limited liability company "Element-Trade". The main activity of the enterprise under study is retail trade (sale of food products, household goods).
The subject of research in this paper is the process of making managerial decisions in this organization.
The theoretical and methodological basis for writing this term paper was the works of the following domestic authors: Pirogova E. V., Ivasenko A. G., Zlobina, N. V., Lysov O. E. and others, as well as foreign authors: Meskon M. H., Albert M., Hedouri F.
The following research methods were used to write the work: the method of a systematic and integrated approach, system analysis, elemental analysis, observation, etc.
The goal, objectives, subject and object of research predetermined the logic of presentation and the structure of this course work, consisting of an introduction, three chapters and a conclusion. The course work is presented on 59 sheets of typewritten text, contains 4 figures, 14 tables, 1 application.
The first chapter "Theoretical foundations of the process of making managerial decisions" considers the essence and significance of managerial decisions, the stages of the process of making managerial decisions in an organization, the methodology for assessing the effectiveness of the process of making managerial decisions.
In the second chapter "Analysis of the management decision-making process in Element-Trade LLC," an analysis of the financial condition of Element-Trade LLC, as well as an analysis of the management decision-making process in Element-Trade LLC and an assessment of the effectiveness of this process.
In the third chapter, "Measures to improve the process of making managerial decisions in Element-Trade LLC," ways to improve the process of making managerial decisions are proposed.
In conclusion, the main conclusions of the study are presented.
Chapter 1. Theoretical foundations of the organization of methods for making management decisions
1.1 The essence and significance of management decisions
Management decision-making processes occupy a central place in the structure of management activities, because it is they who determine to the greatest extent both the content of this activity and its results. The manager has the power, the authority to make decisions, he is also responsible for its implementation, for the use of resources, for the fate of people.
Management decisions are related to the performance of management functions, including planning, organization, coordination and control of any processes. These decisions are implemented in the form of orders, business conversations, instructions, etc. However, not every decision developed and implemented by a leader is managerial.
Management decisions are distinguished by:
Goals. The subject of management (an individual or a group) makes a decision based not on their own interests and needs (although their influence plays a certain role), but in order to solve the problems of a particular organization.
Scale and consequences. The private choice of an individual affects his own life and may affect the few people close to him. A manager, especially a high-ranking one, chooses the course of action not only for himself, but also for the organization as a whole and its employees, and his decisions can significantly affect the lives of many people. If the organization is large and influential, the decisions of its leaders can seriously affect the socio-economic situation of entire regions.
Division of labor. If in privacy When a person makes a decision, as a rule, he fulfills it himself, then there is a certain division of labor in the organization: some employees (managers) are busy solving emerging problems and making decisions, while others (executors) are busy implementing decisions already made.
Professionalism. In private life, each person independently makes decisions by virtue of his intellect and experience. In managing an organization, decision-making is a much more complex, responsible and formalized process that requires professional training. Not every employee of the organization, but only those with certain professional knowledge, experience and skills and occupying the appropriate position, is empowered to make certain decisions independently.
Having considered these distinctive features decision-making in organizations, we can say that a managerial decision is a choice of an alternative made by a decision maker within his authority and competence and aimed at achieving the goals of the organization.
The need for decision-making arises at all stages of the management process and is associated with all areas and aspects of management activities. The decision-making process quite accurately reflects the real problems, relationships and connections that have developed in the organization, and their continuous sequence characterizes the continuity of the management process. Moreover, only the study of the process of developing and implementing solutions makes it possible to evaluate the content side of management, because the content of management is revealed in the content of decisions made. That is why it is so important to understand the essence of decisions.
The economic essence of a management decision is manifested in the fact that the preparation and implementation of any management decision requires financial, material and other costs. Every management decision has a real value. The implementation of an effective management decision will bring the company direct or indirect income, and an erroneous decision will bring losses.
The organizational essence of the management decision is that the company's personnel are involved in this work. For effective work, it is necessary to form a workable team, develop instructions, regulations, empower employees, rights, duties and responsibilities, establish a control system, allocate the necessary resources, including information, provide employees necessary equipment and technology, to coordinate their work. The organizational aspect is manifested in the organization of both the development and implementation of a management decision. At the same time, a number of its functions are realized, namely, guiding, coordinating and motivating.
The guiding function of decisions is manifested in the fact that they are the guiding basis for the implementation of the general functions of management - planning, organization, control, motivation.
The coordinating role of decisions is reflected in the need to coordinate the actions of executors in order to implement decisions within the approved deadlines and of the appropriate quality.
The motivating function of decisions is implemented through a system of organizational measures (orders, resolutions, orders), economic incentives (bonuses, allowances), social assessments(moral and political factors of labor activity: self-affirmation of personality, creative self-realization).
The social essence of a managerial decision lies in the mechanism of personnel management, which includes levers of influence on a person to coordinate their activities in a team. These levers include human needs and interests, motives and incentives, attitudes and values.
The legal essence of the management decision lies in the strict observance of the legislative acts of the Russian Federation and its international obligations, statutory and other documents of the company itself.
The technological essence of a management decision implies the possibility of providing personnel with the necessary technical, information tools and resources for the preparation and implementation of a management decision.
A managerial decision is a choice of an alternative made by a manager within the framework of his official powers and competence and aimed at achieving the goals of the organization; action to resolve a problem.
Management decisions serve as an integral part of any function of the management process and permeate all management activities - from the formulation of a goal to the moment it is achieved. The decision is the main product of the manager's work. The success of the business depends on the effectiveness of management decisions. Therefore, each management decision must be scientifically substantiated and made in a timely manner, comply with the situation and legislative acts, meet the objective conditions for the development of enterprises, ensure the most complete achievement of the goal and rational use resources.
As a rule, some of the decisions made are not feasible. This happens for various reasons: the absurdity of goals, the complexity of control, the lack of deadlines, the assignment of responsibility to specific individuals. In fact, the above points to shortcomings in management activities that lead to serious economic and social consequences (lost opportunities, waste of time and money, irresponsibility, reduced labor activity, decomposition of a healthy psychological climate a team). Therefore, the organization of a deep study of management decisions, competent design and observance of the methodological principles for carrying out this work are of particular relevance.
The management cycle always begins with setting goals and identifying problems, continues with the development and adoption of the necessary solution, and ends with the organization and control of its implementation. Analysis of the result obtained serves as a source for identifying new problems and making new decisions, thus resuming the management cycle. The scheme of this process is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Diagram of the control loop
This shows that any control implements a sequence of three main stages:
determines the state of the managed object (problem identification);
develops an optimal impact for a given state (development and decision-making);
implements it (implementation of the solution).
The management decision is formulated as:
A product of managerial work, an organizational response to a problem that has arisen;
Selecting a specific course of action from possible options; the choice of a previously meaningful goal, means and methods for achieving it;
The choice of a method of action that guarantees a positive outcome of a particular operation.
The managerial decision at the enterprise is a creative act of the subject of management (individual or group person), which determines the program of the team's activities to effectively resolve the urgent problem based on knowledge of the objective laws of the functioning of the controlled system and the analysis of information about its state.
Thus, a managerial decision is associated with the performance of managerial functions, including planning, organization, coordination and control of any processes. Solutions are implemented in the form of orders, business conversations, instructions, etc.
A managerial decision is a choice of an alternative made by a decision maker within the framework of his authority and competence and aimed at achieving the goals of the organization.
The need for decision-making arises at all stages of the management process and is associated with all areas and aspects of management activities. The decision-making process quite accurately reflects the real problems, relationships and connections that have developed in the organization, and their continuous sequence characterizes the continuity of the management process.
The development of effective solutions is the basis for ensuring the competitiveness of products and firms in the market, the formation of rational organizational structures, and the implementation of the correct personnel policy and work, regulation of socio-psychological relations at the enterprise, creation of a positive image.
Deficiencies in managerial activity lead to serious economic and social consequences (missed opportunities, waste of time and money, irresponsibility, reduced labor activity, decomposition of a healthy psychological climate in the team). Therefore, the organization of a deep study of management decisions, competent design and observance of the methodological principles for carrying out this work are of particular relevance.
Management decisions act as a way of constant influence of the control system on the controlled one (the subject on the control object), which ultimately leads to the achievement of the set goals. This is a permanent link between the two subsystems, without which the enterprise as a system cannot function. This circumstance emphasizes the determining place of the managerial decision in the management process.
1.2 Stages of the process of making managerial decisions in an organization
Solving a problem very often requires not a single solution, but a certain sequence of solutions and their implementation. Therefore, a decision is not a one-time act, but the result of a process that develops over time and has a certain structure.
The management process consists of repetitive decision-making processes related to the performance of managerial functions. In the process of performing management functions, managers have to make a large number of decisions, carrying out planning, organizing work, motivating people employed in the organization, controlling and coordinating all the processes that take place in it.
The simplest decision-making scheme assumes that the process is a movement from one stage to another; after identifying the problem and establishing the conditions and factors that led to its occurrence, solutions are developed, from which the best is selected. The number of options developed and considered depends on many factors, and above all on the time, resources and information available to developers. The main constraint is the time within which a decision must be made. Therefore, in parallel with the development of options, they are evaluated, and the final decision is made by choosing the best of those that were prepared and considered in the planned period of time.
The most complete and visual representation of the decision-making process is given by the diagram shown in Figure 2, which reflects its main stages and the order in which they follow.
Rice. 2. The process of making a managerial decision
For the need to make a management decision, a signal is needed about an external or internal influence that has caused or is capable of causing a deviation from the specified mode of the system's functioning, i.e. presence of a managerial situation. Therefore, one of the most important conditions for the adoption right decision is the analysis of the situation. Analysis of the management situation requires the collection and processing of information. This stage performs the function of the organization's perception of the external and internal environment. Data on the state of the main environmental factors and the state of affairs in the organization are received by managers and specialists who classify, analyze information and compare the actual values of controlled parameters with planned or predicted ones, which in turn allows them to find out the problems that should be solved. For the need to make a management decision, a signal is needed about an external or internal influence that has caused or is capable of causing a deviation from the specified mode of the system's functioning, i.e. presence of a managerial situation. Therefore, one of the most important conditions for making the right decision is to analyze the situation.
The first step towards solving a problem is its definition or diagnosis, complete and correct. The problem is the discrepancy between the desired and actual state of the managed object. Identifying and formulating a problem is a complex procedure. The fact is that at the time of their emergence, many of the most important problems are poorly structured, i.e. do not contain obvious goals, alternative ways to achieve them, ideas about the costs and effects associated with each of the options. And bringing these problems to quantitative certainty (structuring) requires from managers not only knowledge and experience, but also talent, intuition, and creativity. We must also not forget that all elements and activities in the organization are interconnected and the solution of any problem in one part of the organization can cause problems in others. Therefore, when defining the problem to be solved, one should strive to ensure that the number of newly emerging problems is minimal.
Definition of selection criteria. Before considering possible solutions to the problem, the manager needs to determine the indicators by which alternatives will be compared and the best choice will be made. These indicators are called selection criteria.
The next stage is the development of a set of alternative solutions to the problem, ideally it is desirable to identify all possible alternative routes solution to the problem, only in this case the solution can be optimal. However, in practice, the leader does not and cannot have such stocks of knowledge and time to formulate and evaluate every possible alternative. Therefore, he usually limits the number of comparison options to just a few alternatives that seem to be the most suitable.
Choice of an alternative. If the problem has been correctly identified and alternative solutions have been carefully weighed and evaluated, it is relatively easy to make a choice, that is, to make a decision. The manager simply chooses the alternative with the most favorable overall consequences. However, if the problem is complex and many trade-offs have to be taken into account, or if information and analysis are subjective, it may happen that no alternative is available. the best choice. In this case, good judgment and experience play a major role.
Although it is ideal for a manager to achieve an optimal solution, the manager, as a rule, does not dream of such in practice. Usually the optimal solution is not found due to time constraints and the inability to take into account all relevant information and alternatives. Because of these limitations, the leader tends to choose a course of action that is obviously acceptable, but not necessarily the best possible.
IN modern systems management, as a result of the division of labor, a situation has developed in which some employees of the organization prepare, develop a decision, accept or approve others, and still others carry out. In other words, the manager often approves and bears responsibility for a solution that he did not develop, the specialists who prepared and analyzed the solution do not participate in its implementation, and the performers do not take part in the preparation and discussion of the decisions being prepared. Management decision-making in an organization is often mistakenly viewed as an individual rather than a group process. It is the organization, and not the individual leader, who must respond to emerging problems. And not one leader, but all members of the organization should strive to improve the efficiency of its work. Of course, managers choose the course for the organization, but for the decision to be implemented, the joint action of all members of the organization is necessary. Therefore, the stage of coordination plays a very significant role in group decision-making processes. Recognition of a solution is rarely automatic, even if it is clearly a good one. The probability of quick and effective implementation increases significantly when the performers have the opportunity to express their opinion, make suggestions, comments.
The process of solving a problem does not end with the choice of an alternative: to obtain a real effect, the decision made must be implemented. This is what is main task implementation management phase.
For the successful implementation of the solution, first of all, it is necessary to determine the complex of works and resources and distribute them according to the performers and deadlines, i.e. foresee who, where, when and what actions should be taken and what resources are needed for this. If it's enough big decisions, this may require the development of a program to implement the solution. During the implementation of this plan, the leader must monitor how the decision is being implemented, provide assistance if necessary, and make certain adjustments.
Even after the decision is finally put into effect, the decision-making process cannot be considered completely completed, because. it remains to be seen whether it justifies itself. This goal is served by the control stage, which performs the function of feedback in this process. At this stage, the consequences of the decision are measured and evaluated, or the actual results are compared with those that the manager hoped to receive. It should not be forgotten that the solution is always temporary. The term of its effective action can be considered equal to the period of relative constancy of the problem situation. Outside it, the solution may cease to have an effect and even turn into its opposite - not to contribute to the solution of the problem, but to exacerbate it. In this regard, the main task of control is to timely identify the decreasing effectiveness of the decision and the need to correct it or make a new decision. In addition, the implementation of this stage is a source of accumulation and systematization of experience in decision-making.
Each organization has features of making managerial decisions, determined by the nature and specifics of its activities, organizational structure, system of intracompany communication. However, the process of developing a management decision has something in common for an organization. We must also not forget that all elements of the organization's activities are interconnected and the solution of any problem in one part of the organization can cause problems in others. Therefore, when defining a solution to a problem, one should strive to ensure that the number of newly emerging problems is minimal.
So, the management process consists of repetitive decision-making processes related to the performance of managerial functions.
For the need to make a management decision, a signal is needed about an external or internal influence that has caused or is capable of causing a deviation from the specified mode of system operation.
Before considering possible solutions to the problem, the manager needs to determine the indicators by which alternatives will be compared and the best choice will be made.
The next stage is the development of a set of alternative solutions to the problem, ideally it is desirable to identify all possible alternative solutions to the problem, only in this case the solution can be optimal.
For the successful implementation of the solution, it is necessary to determine the set of works and resources and distribute them by performers and deadlines, i.e. foresee who, where, when and what actions should be taken and what resources are needed for this. During the implementation of this plan, the leader must monitor how the decision is being implemented, provide assistance if necessary, and make certain adjustments.
Even after the decision is finally put into effect, the decision-making process cannot be considered completely completed, because. it remains to be seen whether it justifies itself. This goal is served by the control stage, which performs the function of feedback in this process. At this stage, the consequences of the decision are measured and evaluated, or the actual results are compared with those that the manager hoped to receive. The main task of control is to timely identify the decreasing effectiveness of the solution and the need to correct it or make a new decision.
1.3 Methodology for assessing the effectiveness of the management decision-making process
Decision-making is the main tool for managing influence, because it is in the development of decisions, their adoption, organization and control that the activity of the entire management apparatus lies. The effectiveness of management decisions is the main characteristic of the decisions made, which is determined by the quality of the decision, its impact on improving performance, as well as the emotional agreement of the performers with it. Evaluation of the effectiveness of managerial decision-making plays an important role in the activities of the entire enterprise as a whole. It is necessary for further work organization, because if the decision made turns out to be ineffective, then the work of all departments will also be ineffective.
It should be noted that for the successful implementation of the decisions made, the organization must have a mechanism for their implementation, the main tasks of which are: development of an implementation program, management of implementation, control over execution, evaluation of results. Designing and implementing solutions that provide always high performance is a very difficult task even for experienced managers. The effect of the implementation of a management decision does not always correspond to the expected one, but, despite this, there must be a constant desire to maximize this effect.
The task of determining the effectiveness of managerial decisions is the most complex and controversial problem of management. It is impossible to consider the effectiveness of a management decision and its implementation in isolation. This is due to the fact that the effectiveness of the decision lies not so much in its absolute correctness, but in the fact that, being implemented consistently and on time, it will achieve the goal. Consequently, the effectiveness of managerial decisions depends both on the quality of the decisions themselves and on the quality of their implementation.
Efficiency is understood as the result of activity achieved through the work of the entire team (including employees of the management apparatus), and also efficiency reflects the effectiveness of the actual management activities. In one sense and another, general indicators and a system of particular indicators of economic and social efficiency are used to characterize efficiency.
Figure 3. Calculation scheme for assessing management efficiency
To assess the economic efficiency of management in a broad sense, the following formula is used:
There are a lot of private indicators of the economic efficiency of the work of the labor collective, among them: profitability, turnover, return on investment, capital intensity, capital productivity, labor productivity, the ratio of wage growth and labor productivity, etc.
General indicators of social efficiency in a broad sense can be:
The degree of fulfillment of consumer orders;
The share of the company's sales in the market, etc.
Particular indicators of social efficiency are:
Timeliness of order fulfillment;
Completeness of order fulfillment;
Provision of additional services;
After-sales service, etc.
The generalizing indicator of economic efficiency of management in the narrow sense is calculated in the following way:
Private indicators:
The share of administrative and management expenses in the total cost of the enterprise;
The share of the number of managerial employees in the total number of employees at the enterprise;
Manageability load (actual number of employees per employee of the management apparatus), etc.
Generalizing indicators of social efficiency in the narrow sense are:
The share of decisions taken at the suggestion of employees of the labor collective,
The number of employees involved in the development of a management decision.
Private indicators of social efficiency include: the degree of technical equipment of managerial work, the turnover of employees in the management apparatus, the qualified level of personnel, etc.
It is also legitimate to evaluate the effectiveness of the performance of individual management functions: planning, organization, motivation, control (the work of individual departments of the management apparatus). For this, a set of indicators is also used that reflects the specifics of activities for each management function. So, for example, according to the planning function, the degree of achievement of the set goals (planned tasks) is assessed; according to the function of the organization - the equipment of the enterprise with modern technological equipment, staff turnover; according to the function of motivation - the methods used to influence the team (encouragement, punishment, their ratio); by control function - the number of violations of labor, technological discipline, etc.
Evaluation of management efficiency can be carried out for various calendar periods of time (month, quarter, year). The dynamics of these indicators, as well as comparison with similar data of similar enterprises operating in similar natural-geographical and economic conditions, make it possible to draw a conclusion about the effectiveness of the management apparatus.
So you can evaluate the effectiveness of the work of the management apparatus as a whole, as well as specific decisions. In the first case, efficiency reflects the effectiveness of the management process, which is manifested through a set of decisions made and implemented. In the second case, the assessment methodology outlined is quite acceptable for assessing individual management decisions.
In addition, three groups of indicators (criteria) are taken into account and considered, characterizing:
Time costs (efficiency of the process);
Resource costs and economic result (resource intensity and process efficiency);
The degree of achievement of goals (target effects).
Efficiency of the management process (implementation of strategic changes). It is characterized by the dynamics of indicators of time spent on the performance of systemic functions of the organization.
Depending on the configuration of the control system, some of the functions in its subsystems, in terms of time, can be performed sequentially (i.e., condition each other), and some can be performed in parallel (independently). But in any case, the desire to reduce the complexity of operations in all departments will have a positive effect on the effectiveness of management, its flexibility and maneuverability.
T is an indicator of the complexity of performing managerial functions,
Ср - the number of employees in certain positions:
Feff - effective working time fund of the corresponding calendar period.
So, reducing the complexity of the management operation reduces the need for workforce. This, in turn, will reduce the need for financial resources (in the form of wages, related deductions, administrative and social overheads), material resources (in the form of equipment, auxiliary materials, inventory, space, energy), information resources(in the form of volumes of incoming and outgoing information). Knowing the specific standards for these resources, the approximate prices for them, it is possible to determine the first (reduced) component of the calculation of the effect of direct time savings by calculation.
The same goals can be achieved at different costs, so the main criterion for the effectiveness of a solution is the ratio of the effect obtained as a result of its implementation, expressed as an indicator of the degree of achievement of the goal, to the amount of costs for developing the solution and its implementation. In such situations, one of the most commonly used methods for evaluating the effectiveness of a solution is the "cost-profit" method, in which efficiency is quantitatively characterized by the profit per unit of costs, where "profit" is understood as a certain set of criteria that characterize a particular solution. Such criteria can include both objective indicators, such as payment flows, payback period, profitability, production volume, and others, as well as subjective assessments, such as the social significance of the project, the image of the company, etc.
The effectiveness of a management decision can be divided by the levels of its development and implementation, the coverage of people and companies. The system of quantitative and qualitative assessments based on real indicators, norms and standards manages the effectiveness of a management decision. An important feature of a management decision as a product of management activity is its intangible essence.
The effectiveness of the functioning of the organization to a very large extent depends on the quality of management decisions. This determines the importance of mastering all responsible employees of the administrative apparatus, and above all, the heads of organizations, with theoretical knowledge and practical skills in the development and implementation of optimal management decisions.
Thus, the effectiveness of management decisions is the main characteristic of the decisions made, which is determined by the quality of the decision, its impact on improving performance, as well as the emotional agreement of the performers with it. Evaluation of the effectiveness of managerial decision-making plays an important role in the activities of the entire enterprise as a whole. It is necessary for the further work of the organization, because if the decision made turns out to be ineffective, then the work of all departments will also be ineffective.
The economic efficiency of a management decision is characterized by the ratio of the cost of the surplus product obtained through the implementation of a specific management decision and the costs of its preparation and implementation. Surplus product can be presented in the form of profit, cost reduction, productivity increase, loans, etc.
The social efficiency of a management decision is considered as the result of achieving social goals for a larger number of employees and the company in a shorter time, with a smaller number of employees, and lower financial costs.
The values of the quantities included in the formula can be determined on the basis of operational accounting data and accounting data of the organization.
Evaluation of management efficiency can be carried out for various calendar periods of time (month, quarter, year). The dynamics of these indicators allows us to draw a conclusion about the effectiveness of the management apparatus.
Chapter 2. Analysis of the process of making managerial decisions in Element-Trade LLC
2.1 general characteristics LLC "Element-Trade"
"Element - Trade" is a limited liability company. Legal address of the company: Yekaterinburg, st. Shcherbakova, 4. Postal address of LLC "Element-Trade": Ekaterinburg Sibirsky Trakt 12 building 5. The scope of the company according to the constituent documents:
Retail trade in foodstuffs;
retail trade industrial goods;
retail trade in alcoholic, low-alcohol and non-alcoholic drinks and juices;
Retail sale of tobacco products;
Retail sale of frozen products;
retail trade in animal feed;
production of ready-to-eat products.
The first "Coin" in Yekaterinburg appeared in the spring of 2001. Then two stores were opened: one - Cash & Carry format, the other - an economy class supermarket. The network was founded by the company R-Modul (specialization: trade in cigarettes, chocolate, confectionery). By 2003, there were 6 stores. In 2004, the "Coin" store appeared in Tyumen, N. Tagil. In 2005, retail chain stores appeared in Ufa and Chelyabinsk. 2006 - shops were opened in Kurgan, and 3 new supermarkets appeared. The opening of the 100th store took place in 2007. Also, the trading network began work in the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug and the first store appeared in Moscow. Since 2008, the company's own distribution center. Now suppliers no longer need to deliver goods to stores in small batches. All goods are received by the distribution center, then delivered to the stores of the network. In 2010, there were already 200 stores, and in 2011 the retail chain entered the Siberian Federal District. In 2012, there were 400 stores. As of July 2013, there were 500 stores in the trading network.
Trading network "Monetka" today is one of the leaders in Yekaterinburg and Ural region(supermarkets and discounters). TC "Monetka" stores operate in Chelyabinsk, Tyumen, Kaluga, Vladimir, Kurgan, Moscow, Sverdlovsk regions; Republic of Bashkortostan; in the Perm region; in the Khanty-Mansiysk and Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrugs.
The organizational structure of the enterprise is presented in Appendix 2.
The leadership position belongs to to CEO- one of the founders of the Society. It performs the following functions:
management of company property
sets staffing,
Opens current and other accounts,
issues orders and gives instructions binding on all employees,
determines the structure of the administrative apparatus, the number, qualifications and staffing,
hires (appoints) and dismisses employees of the company,
· signs agreements with partners.
Annex 2 presents not complete structure organizations, store directors report to the regional manager of the respective region. Each store director has two deputies: for the trading floor and for the warehouse, to whom the administrators of the trading floor and warehouse workers report, respectively. Each department in the store (dairy, industrial, confectionery, etc.) has an administrator to whom the sellers of the corresponding department report, cashiers report to the senior cashier.
2.2 Analysis of the financial condition of the enterprise
Analysis economic activity is an important element in the production management system, an effective means of identifying on-farm reserves, management decisions and monitoring their implementation in order to increase the efficiency of the enterprise.
First of all, it is necessary to analyze the balance sheet of Element - Trade LLC, presented in Appendix 1.
The property of the enterprise increased from 2008 to 2012. This happened due to an increase in the cost of current assets, which increased mainly due to an increase in the cost of fixed assets and construction in progress. The following changes occurred in the composition of current assets: stocks decreased by 2012 after some increase in 2009; accounts receivable tend to decrease. Positive dynamics is typical for short-term financial investments, and the amount of funds fluctuates throughout the entire study period.
In general, the value of current assets is reduced.
Sources of formation of property of the organization for the period under review also increased. At the same time, the share of own funds did not change, although retained earnings increased 1.5 times. Long-term liabilities slightly decreased, but short-term loans increased at the same time.
The amount of loans and credits decreases, but the share of accounts payable increases, mainly due to an increase in debt to suppliers and contractors.
The results of the analysis of the profit and loss statement of Element - Trade LLC are shown in table 1.
Table 1
Gains and losses report
|
Absolute indicators, thousand rubles |
||||||
|
1. Sales proceeds |
||||||
|
2. Cost of goods sold |
||||||
|
3. Gross profit |
||||||
|
4. Commercial. expenses |
||||||
|
5. Management expenses |
||||||
|
6. Profit / loss from sales |
||||||
|
Other income and expenses 7. Interest receivable |
||||||
|
8. Interest payable |
||||||
|
9. Other income |
||||||
|
10. Other expenses |
||||||
|
11. Profit/loss before tax |
||||||
|
12. Deferred taxes. assets |
||||||
|
13. Deferred taxes. obligations |
||||||
|
14. Current income tax |
||||||
|
15. Net profit / loss |
The table shows that the amount of profit of Element - Trade LLC fluctuates, but still grows in 2012, this is due to an increase in gross profit. However, management costs are growing, so the amount of profit from sales is not growing as significantly as gross profit. The growth of net profit is positively affected by the increase in other income.
Calculation of indicators financial stability presented in table 2.
table 2
Indicators of financial stability
|
Index |
Optimal meaning |
|||||||
|
Coefficient of autonomy (financial independence) |
||||||||
|
Debt ratio |
1- (s490/s700) |
|||||||
|
Coefficient fin. dependencies |
(s590+s690 - s640-s650) /s490 |
|||||||
|
Coefficient fin. sustainability |
(s490+s590) / s700 |
|||||||
|
Funding ratio |
с490/ (с590+с690) |
|||||||
|
The coefficient of security of own. means |
(s490-s190) /s290 |
|||||||
|
Agility factor |
(s490-190+s510) / s490 |
|||||||
|
Long-term investment structure ratio |
Indicators of the financial stability of an enterprise characterize the structure of the capital used by the enterprise from the standpoint of its solvency and financial stability of development. These indicators make it possible to assess the degree of protection of investors and creditors, as they reflect the company's ability to repay long-term obligations. This group of indicators is also called indicators of the capital structure and solvency or coefficients for managing sources of funds.
The data in the table show that the autonomy coefficient, after a slight decrease by 2010, then rises, almost to the previous level, but always remains below the optimal value. This suggests that the company's assets are formed mainly from borrowed capital, and the company does not have sufficient independence and opportunities to conduct an independent financial policy.
The coefficient of financial dependence shows the amount of funds raised per 1 ruble. own. There are no significant changes in this indicator, and in 2012 the enterprise attracted 3 rubles 62 kopecks for one ruble of its own capital. So, as already noted, the dependence of this enterprise on external sources is great.
The dependence on borrowed funds also confirms the value of the equity financing ratio of borrowed funds.
The coefficient of maneuverability of own funds shows the ability of the enterprise to maintain the level of its own working capital and replenish working capital, if necessary, from its own sources. At this enterprise, this indicator is falling, thus, the ability to replenish working capital at the expense of its own is becoming lower and lower.
The coefficients given in table 3 characterize the efficiency of the enterprise's use of its total assets or any of their types. They show how much revenue each ruble of assets provides, how quickly assets turn around in the course of the enterprise's activities.
Table 3
Business Activity Indicators
|
Index |
Optimal meaning |
|||||||
|
Coef. asset turnover |
accelerating trend |
|||||||
|
Coef. inventory turnover |
accelerating trend |
|||||||
|
return on assets |
||||||||
|
Coef. turning deb. debt |
s010/(s230 +s240) |
|||||||
|
deb circulation time debt |
365*(s230+s240)/ |
|||||||
|
Coef. turning over a loan. debt |
||||||||
|
Loan application time. debt |
||||||||
|
Coef. ratio deb. and credit. debt |
(s230+ s240)/s620 |
|||||||
|
Coef. turnover of finished products |
||||||||
|
Coef. turnover of working capital |
accelerating trend |
|||||||
|
Coef. wrapping own. capital |
||||||||
|
Coef. turning over attracted Fin. capital |
s010/(s510 + s610) |
The asset turnover ratio reflects the rate of turnover of the entire capital of the organization or the efficiency of using all available resources, regardless of their sources. The data in Table 4 show that the organization began to complete the full circulation cycle more slowly, making a profit, but in 2012 there is a tendency to accelerate.
The inventory turnover ratio shows that overstocking either decreases or increases, and the smaller the overstocking, the faster you can pay off debts.
The turnover of receivables and the time of its circulation almost does not change, the average period of time required for the company to receive money after selling products is 47 days. The turnover ratio of accounts payable tends to decrease, and the time of its circulation increases and by 2012 is 171 days. Thus, it can be noted that the turnover of accounts receivable is faster than that of accounts payable, which means that the debts of debtors turn into cash faster. Accordingly, by the time the enterprise needs to pay off creditors, there is no shortage of cash in circulation.
Sustainability financial position organizations and their business activity are characterized by the ratio of receivables and payables. In Element-Trade LLC, accounts payable prevail over receivables, but this predominance is declining and by 2012 is 0.27 rubles. accounts receivable for 1 rub. accounts payable. As we can see, the value of this indicator is lower than the recommended one, and this may be a factor leading to a low level of liquidity. Therefore, despite the higher turnover of receivables, cash in circulation may still not be enough to pay off accounts payable, especially if this indicator continues to decline.
The finished product turnover ratio shows how many times a year finished products. This figure fluctuates. The turnover of working capital practically does not change during the study period, and in 2012 each type of working capital was consumed and renewed once a year. The equity turnover ratio reflects the activity of using cash. The value of this indicator is decreasing, which indicates the inactivity of a part of own funds. And the rate of turnover of attracted capital, on the contrary, increases.
Similar Documents
The essence of management decisions, their classification and typology. Decision-making process, principles and stages. Analysis of the process of making managerial decisions in LLC Household appliances. Ways to improve the efficiency of decision-making in the activities of the enterprise.
term paper, added 01/26/2015
Classification of management decisions and the essence of a systematic approach. Comparative characteristics of management decision-making methods. SWOT-analysis and assessment of the management decision-making system at the enterprise, reserves for improving its efficiency.
graduate work, added 05/15/2012
Basic concepts, classification groups and types of management decisions. The essence of decisions and the order of their development. Evaluation of the effectiveness of managerial decision-making and methods of their analysis. Making a decision on the example of the company LLC "Your sausages".
term paper, added 06/19/2011
Determination of indicators of the balance structure, economic efficiency, financial stability of the enterprise as the basis for making management decisions. System non-material motivation workers' labor. Analysis of the strengths and weaknesses of the enterprise.
practice report, added 05/16/2013
thesis, added 12/25/2010
The essence of managerial decision-making, their characteristic features and classification. Detailed structuring of the decision-making process. The logic of management activity. Experience in the adoption of management technologies on the example of the company CJSC "Vneshtorgsib-M".
thesis, added 12/26/2010
The value of the analysis of the internal environment for effective management decision-making. Methodology and stages of conducting a SWOT analysis of an organization. Diagnostics of the resource potential of an enterprise (value system). Strategic Analysis the competitive position of the firm.
term paper, added 09/26/2010
The essence of management decisions, the requirements for them. Classification of management decisions. Foreign experience participation of the manager in the decision-making process. Analysis of the quality of managerial decisions made in the JV "KOP" JSC "ORS Gomel".
term paper, added 06/13/2016
The concept and classification of business processes of management decisions. Application of methods for improving the business decision-making process. Analysis of the most popular and relevant management decisions, their effectiveness and recommendations proposed for them.
thesis, added 03/31/2018
The process of making managerial decisions. Formation of goals, criteria and restrictions. Swot-analysis of the activities of LLC "OP AN-Security". Building a decision tree. Problems and methods of multicriteria optimization. Evaluate decisions in terms of spending money.