How to make a paper prism Volume and surface area of a regular quadrangular prism Using a crystal prism to create a rainbow
Given:
Intersection of pyramid and prism
Necessary:
Build a sweep of a straight prism and show on it the line of intersection of the prism with the pyramid.
Building a straight prism sweep is much easier than a pyramid sweep.
Construction of a prism scan
The construction of a sweep of a straight prism is facilitated by the fact that all dimensions for the sweep are taken from diagrams and we do not need to find the natural dimensions of the edges of the prism. Since a straight prism is given, the lateral edges of the prism are projected onto the frontal projection plane in full size. The edges of the bases of a straight prism are parallel to the horizontal plane of projections and are also projected onto it in full size.
Algorithm for constructing a prism scan
- We draw a horizontal line.
- From an arbitrary point G of this line, we set aside the segments GU, UE, EK, KG equal to the lengths of the sides of the base of the prism.
- From points G, U, ..., perpendiculars are restored and quantities equal to the height of the prism are laid on them. The resulting points are connected by a straight line. Rectangle GG1G1G is a development of the side surface of the prism. To indicate on the development of the faces of the prism from the points U, E, K, perpendiculars are restored.
- To obtain a complete development of the surface of the prism, the polygons of its bases are attached to the development of the surface.
To build on the scan the line of intersection of the prism with the pyramid of closed broken lines 1, 2, 3 and 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, we use vertical straight lines.
More details in the video tutorial on descriptive geometry in AutoCAD
At the heart of a geometric body - a prism - are polygons, and each side face is a parallelogram. The uninitiated may have been a little scared. But if your child is asked to come to a lesson with a prism, you will naturally want to help him and explain how to make a paper prism.
Let's start by making a straight prism. In this prism, the side edges are perpendicular to the bases. The easiest to make with your own hands is a paper prism with three faces, since its bases are the simplest of polygons - triangles. Let's make a "correct" prism. Its bases are represented by equilateral triangles.
triangular prismLet's think about the height of our triangular paper prism. Let's draw a rectangle with one side equal to the height, and the other equal to the length of the perimeter of the triangle at the base. The resulting rectangle is divided by parallel lines into three equal parts. From the corners of the rectangle located in the middle, we draw circles with a compass with a radius equal to the side of our triangle at the base. Where the circles intersect outside the original rectangle, put points and connect them to the centers of the circles. We should get the figure shown in the middle of the picture. Next, we cut out the figure with small allowances for gluing, bend along the existing straight lines and get the finished prism.
According to what template a paper prism with four faces is made, the diagram in the figure clearly demonstrates.
 Hexagonal prism
Hexagonal prism
An example of a blank for a five-sided prism is shown in the figure.  Here the height of the pyramid is 10 cm, the length of the sides of the pentahedron at the base is 3 cm. Similarly, a hexagonal paper prism can be made, but at its base lies a hexagon.
Here the height of the pyramid is 10 cm, the length of the sides of the pentahedron at the base is 3 cm. Similarly, a hexagonal paper prism can be made, but at its base lies a hexagon.
An inclined paper prism is shown in this figure.  Its side faces are at an angle to the base. Such a prism can be made according to a scanning template.
Its side faces are at an angle to the base. Such a prism can be made according to a scanning template.
Your privacy is important to us. For this reason, we have developed a Privacy Policy that describes how we use and store your information. Please read our privacy policy and let us know if you have any questions.
Collection and use of personal information
Personal information refers to data that can be used to identify or contact a specific person.
You may be asked to provide your personal information at any time when you contact us.
The following are some examples of the types of personal information we may collect and how we may use such information.
What personal information we collect:
- When you submit an application on the site, we may collect various information, including your name, phone number, email address, etc.
How we use your personal information:
- The personal information we collect allows us to contact you and inform you about unique offers, promotions and other events and upcoming events.
- From time to time, we may use your personal information to send you important notices and messages.
- We may also use personal information for internal purposes, such as conducting audits, data analysis and various research in order to improve the services we provide and provide you with recommendations regarding our services.
- If you enter a prize draw, contest or similar incentive, we may use the information you provide to administer such programs.
Disclosure to third parties
We do not disclose information received from you to third parties.
Exceptions:
- In the event that it is necessary - in accordance with the law, judicial order, in legal proceedings, and / or based on public requests or requests from state bodies in the territory of the Russian Federation - disclose your personal information. We may also disclose information about you if we determine that such disclosure is necessary or appropriate for security, law enforcement, or other public interest reasons.
- In the event of a reorganization, merger or sale, we may transfer the personal information we collect to the relevant third party successor.
Protection of personal information
We take precautions - including administrative, technical and physical - to protect your personal information from loss, theft, and misuse, as well as from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration and destruction.
Maintaining your privacy at the company level
To ensure that your personal information is secure, we communicate privacy and security practices to our employees and strictly enforce privacy practices.
It is necessary to build a development of the faceted bodies and draw on the development the line of intersection of the prism and the pyramid.
To solve this problem in descriptive geometry, you need to know:
- information about the development of surfaces, methods of their construction and, in particular, the construction of developments of faceted bodies;
- one-to-one properties between a surface and its unfolding and methods for transferring points belonging to the surface to the unfolding;
- methods for determining the natural values of geometric images (lines, planes, etc.).
Procedure for solving the Problem
The scan is called a flat figure, which is obtained by cutting and unbending the surface until it is completely aligned with the plane. All surface unfolds ( blanks, patterns) are built only from natural values.
1. Since the scans are built from natural values, we proceed to determine them, for which a tracing paper (graph paper or other paper) of A3 format is transferred task No. z with all points and lines of intersection of polyhedra.
2. To determine the natural values of the edges and the base of the pyramid, we use right triangle method. Of course, others are possible, but in my opinion, this method is more intelligible for students. Its essence lies in the fact that “on the constructed right angle, the projection value of the straight line segment is plotted on one leg, and on the other, the difference in the coordinates of the ends of this segment, taken from the conjugate projection plane. Then the hypotenuse of the resulting right angle gives the natural value of this line segment..
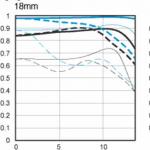
Fig.4.1

Fig.4.2

Fig.4.3
3. So, in the free space of the drawing (Fig.4.1.a) making a right angle.
On the horizontal line of this angle, we set aside the projection value of the edge of the pyramid DA taken from the horizontal projection plane - lDA. On the vertical line of the right angle, we plot the difference in the coordinates of the points D’ andA’ taken from the frontal projection plane (along the axis z way down) - . Connecting the obtained points with a hypotenuse, we obtain the natural size of the edge of the pyramid | DA| .
Thus, we determine the natural values \u200b\u200bof other edges of the pyramid D.B. and DC, as well as the base of the pyramid AB, BC, AC (fig.4.2), for which we construct the second right angle. Note that the definition of the natural size of the edge DC is made in those cases when it is given in projection on the original drawing. This is easily determined if we remember the rule: if a straight line on any projection plane is parallel to the coordinate axis, then on the conjugate plane it is projected in full size.
In particular, in the example of our problem, the frontal projection of the edge D’ C’ parallel to axis X, therefore, in the horizontal plane DC immediately expressed in natural size | DC| (fig.4.1).

Fig.4.4
4. Having determined the natural values of the edges and the base of the pyramid, we proceed to the construction of a sweep ( fig.4.4). To do this, on a sheet of paper closer to the left side of the frame, we take an arbitrary point D considering that this is the top of the pyramid. Draw from a point D arbitrary straight line and set aside on it the natural size of the edge | DA| , getting a point BUT. Then from the point BUT, taking on the solution of the compass the full size of the base of the pyramid R=|AB| and placing the leg of the compass at the point BUT we make an arc. Next, we take on the solution of the compass the full size of the edge of the pyramid R=| D.B.| and placing the leg of the compass at the point D we make a second arc notch. At the intersection of arcs we get a point AT, connecting it with points A and D get the edge of the pyramid DAB. Similarly, we attach to the edge D.B. facet DBC, and to the edge DC- edge DCBUT.
To one side of the base, for example ATC, we attach the base of the pyramid also by the method of geometric serifs, taking the size of the sides on the compass solution BUTBandAFROM and making arc serifs from points BandC getting a point A(fig.4.4).
5. Building a sweep prism is simplified by the fact that in the original drawing in the horizontal plane of projections the base, and in the frontal plane - 85 mm high, it set at full size
To build a sweep, we mentally cut the prism along some edge, for example, along E, having fixed it on the plane, we will expand the other faces of the prism until it is completely aligned with the plane. It is quite obvious that we will get a rectangle whose length is the sum of the lengths of the sides of the base, and the height is the height of the prism - 85mm.
So, to build a sweep of the prism, we proceed:
- on the same format where the pyramid was built, on the right side we draw a horizontal straight line and from an arbitrary point on it, for example E, successively lay off the segments of the base of the prism EK, KG, GU, UE, taken from the horizontal projection plane;
- from points E, K, G, U, E we restore the perpendiculars, on which we set aside the height of the prism, taken from the frontal projection plane (85mm);
- connecting the obtained points with a straight line, we obtain a development of the side surface of the prism and to one of the sides of the base, for example, GU we attach the upper and lower bases using the method of geometric serifs, as was done when building the base of the pyramid.

Fig.4.5
6. To build a line of intersection on the development, we use the rule that "any point on the surface corresponds to a point on the development." Take, for example, the edge of a prism GU where the line of intersection with the points 1-2-3 ; . Set aside on the development of the base GU points 1,2,3 by distances taken from the horizontal projection plane. Restore the perpendiculars from these points and plot the heights of the points on them 1’ , 2’, 3’ , taken from the frontal projection plane - z 1 , z 2 andz 3 . Thus, we got points on the sweep 1, 2, 3, connecting which we get the first branch of the line of intersection.
All other points are transferred similarly. The constructed points are connected, getting the second branch of the line of intersection. Highlight in red - the desired line. Let us add that in case of incomplete intersection of faceted bodies, there will be one closed branch of the intersection line on the development of the prism.
7. The construction (transfer) of the intersection line on the development of the pyramid is carried out in the same way, but taking into account the following:
- since the sweeps are built from natural values, it is necessary to transfer the position of the points 1-8 lines of intersection of projections on the lines of edges of natural sizes of the pyramid. To do this, take, for example, the points 2 and 5 in the frontal projection of the rib DA we transfer them to the projection value of this right angle edge (fig.4.1) along communication lines parallel to the axis X, we get the required segments | D2| and |D5| ribs DA in natural values, which we set aside (transfer) to the development of the pyramid;
- all other points of the intersection line are transferred in the same way, including points 6 and 8 lying on the generators Dm and Dn why right angle (fig.4.3) the natural values of these generators are determined, and then points are transferred to them 6 and 8;
- on the second right angle, where the natural values \u200b\u200bof the base of the pyramid are determined, points are transferred mandn intersections of generators with the base, which are subsequently transferred to the development.
Thus, the points obtained on natural values 1-8 and transferred to the development, we connect in series with straight lines and finally we get the line of intersection of the pyramid on its development.
Section: Descriptive geometry /This image is a "regular" street photo. Overpasses lead the eye to the image ... through a prism
A key element of any photography is how you use light. In this article, you will learn how to split it. The use of a prism in photography provides new opportunities and is another way to use the refraction of light.
What does a prism do to light?
Since the prism is a glass object, light refracts as it passes through it, creating several effects that you can use in photography.
There are two ways to use a prism.
- Rainbow projection - a prism, and in particular its triangular shape, acts by dividing the light and revealing waves of various lengths in the form of a rainbow. And you can take a picture of it.
- Light Redirection - Light can change direction abruptly when passing through a prism. This means that when you look through it, you will be able to see the painting at a 90 degree angle to yourself. This factor makes it possible to create a double exposure.

The picture clearly shows the rainbow light from the prism, as well as the remnants of light emitted at different angles.
Using a Crystal Prism to Create a Rainbow
A great way to use a prism is to create a rainbow. The larger the prism, the larger the resulting rainbow. Another way to increase its size is to increase the distance between the prism and the surface you are projecting the rainbow onto. The difference between these options is that as the aforementioned distance increases, the rainbow light becomes more diffuse and less intense.

Using a prism, you can create your own rainbow
Notice also how high the sun is in the sky. The angle at which sunlight strikes the prism affects the angle of the projected rainbow. It is easier to project a rainbow onto the ground at noon. To project a rainbow more horizontally, you need to photograph when the sun is lower in the sky, i.e. after sunrise or before sunset.
rainbow as photo detail
Rainbow light is very colorful and when projected onto a surface it can create an interesting effect. Look for a surface that has a neutral color (such as gray or white). Pay attention to surfaces with a pleasant texture.
Spin the prism until you can see the rainbow projected onto the surface you are photographing. You can, of course, take a picture by holding the prism and the camera. But it's good if you have a friend to help. Since this is a detailed photo, it is better to use a macro lens, but you can find equally interesting compositions using other lenses.
rainbow in portrait photography
Undoubtedly, one of the most popular forms of prism photography is projecting a rainbow onto the model's face. The rainbow won't end up being big, and it would be nice, again, to have another person hold the prism while you take the picture.
Three images in one frame
You can shoot through the glass those objects that appear inside the prism. Raise the prism and rotate it. You will see images inside. However, they will not be the same as those directly in front of you. Depending on how you rotate the glass prism, one or two images will be visible. These are the ones you can work with to create a one-click shutter.
Lens selection
For prism photography - wide angle and macro lenses.
- The wide-angle lens allows you to add a background image to your photo. However, the edge of the prism becomes more visible in the frame. It's not easy to blur an image with the aperture available on most wide-angle lenses.
- macro lens Most prism photography is done with it, as this lens allows you to focus close to the prism and avoid trapping your hand in the frame. The transition from the background to the prism image is also harder to detect.

The image was taken with a macro lens with a prism, and in the end it looks like an optical illusion.
Aperture for prism photography
Which one you use for these photos depends mostly on what you plan to do with the background and how sharp you want the image to be in the prism.
An open aperture of f/2.8 or more will certainly work to blur the background. Most photographs to achieve the feeling of multiple exposure. This means that an aperture of around f/8 is the right balance between background and detail, and avoids the prism line being too harsh when transitioning to the background.
background image
Due to the small width of the prism, even with a macro lens, the background takes up most of the frame. So what works as a backdrop for this type of photo?
- Leading lines - the background that draws attention to the images inside the prism - is used effectively. It could be a tunnel or a road leading to infinity.
- The texture background is more of a blank canvas for images in a prism. It can be a brick wall or leaves and flowers.
- Symmetry. Since the prism splits your image down the middle, using symmetry on both sides of that split is a pretty effective strategy.

Using background symmetry can work well in prism photography.
Image in glass
Now the hard part is getting a good image inside the prism. The images in it may be at 90 degrees to where you are looking, or perhaps at 60 degrees to the edge and in front of where the photographer is standing. Incorporating this into background composition is a tricky aspect of prism photography.
- Composition - You already have a good composition for your background. Now we need to save it while adding a point of interest that would look good through a prism. Just use trial and error. Change the angle of the prism or rotate it; You can also try stepping back and forth.
- Adding a model. An easier way to add interest to an image in a prism is to take it as a portrait photo. The advantage is that you can simply ask the model to stand in the desired position from which the refracted light passes through the prism.

Adding a model to the composition of this image made the sakura photo much more interesting.
Use fractals
Fractals are another element that uses refraction in photography. They produce prismatic effects, but are not triangular in themselves. You can shoot through them without worrying about the images being at a 90 degree angle to you. Fractals are often used to create creative soft-edged portrait photos or other abstract shots.
Time to go and share the light!
If you want to try something new in photography, you will definitely love . It's a bit difficult to photograph with her, but that's what makes the process really interesting. Right now it's time to take a crystal prism in your hands and go towards experiments!